
Semantic Layer for SaaS: Why It Matters
Business Intelligence
Dec 18, 2025
How a semantic layer standardizes SaaS metrics, enables self-serve queries, enforces governance, and improves AI accuracy and query performance.
A semantic layer simplifies how SaaS companies access and use their data. It bridges the gap between raw data and business users by standardizing key metrics like monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or customer churn rate. This ensures everyone in the organization works with consistent, accurate data, reducing confusion and enabling faster decisions.
Key Benefits:
Consistency Across Teams: Metrics are defined once, eliminating conflicting calculations.
Self-Serve Data Access: Non-technical users can query data without needing SQL expertise by using natural-language interfaces.
AI-Driven Insights: AI tools provide reliable answers by using pre-validated business logic.
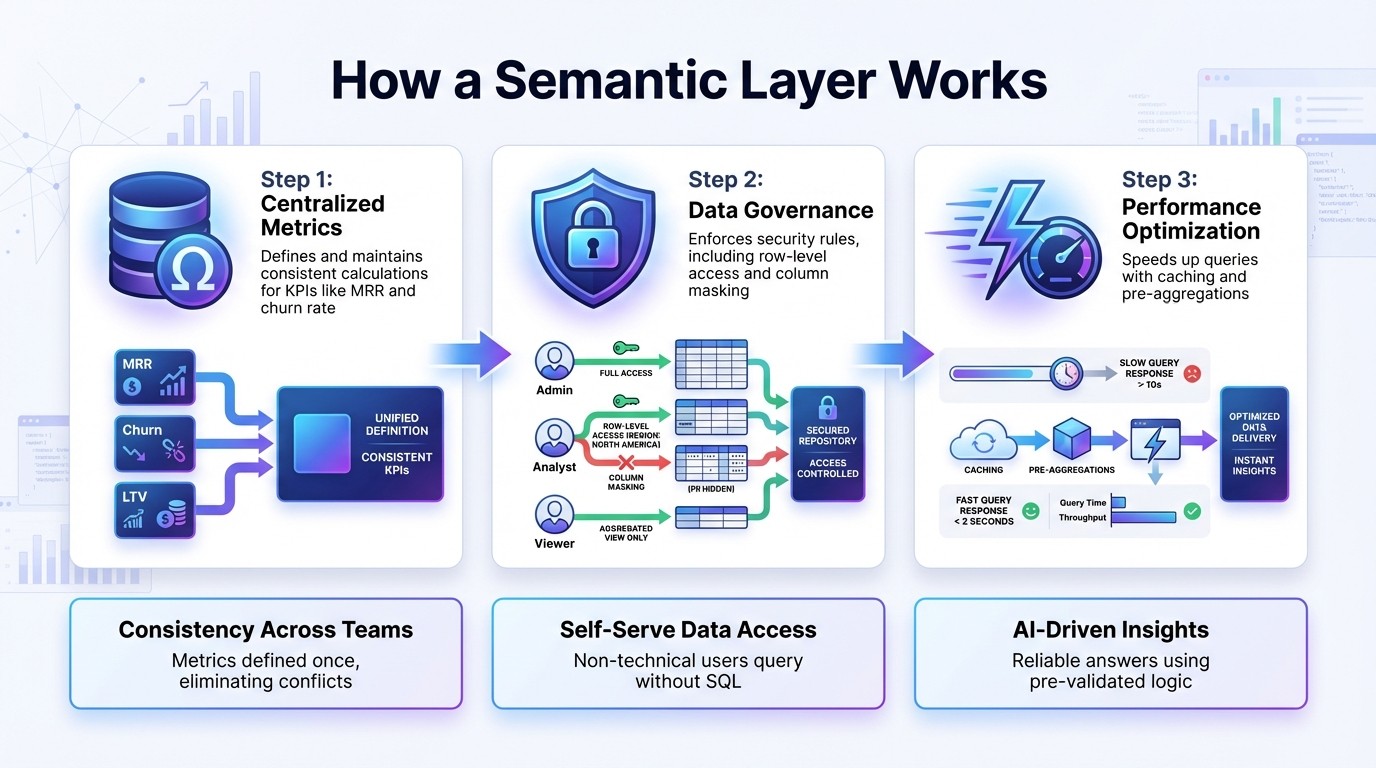
How It Works:
Centralized Metrics: Defines and maintains consistent calculations for KPIs.
Data Governance: Enforces security rules, like row-level access and column masking.
Performance Optimization: Speeds up queries with caching and pre-aggregations.
Example: Querio
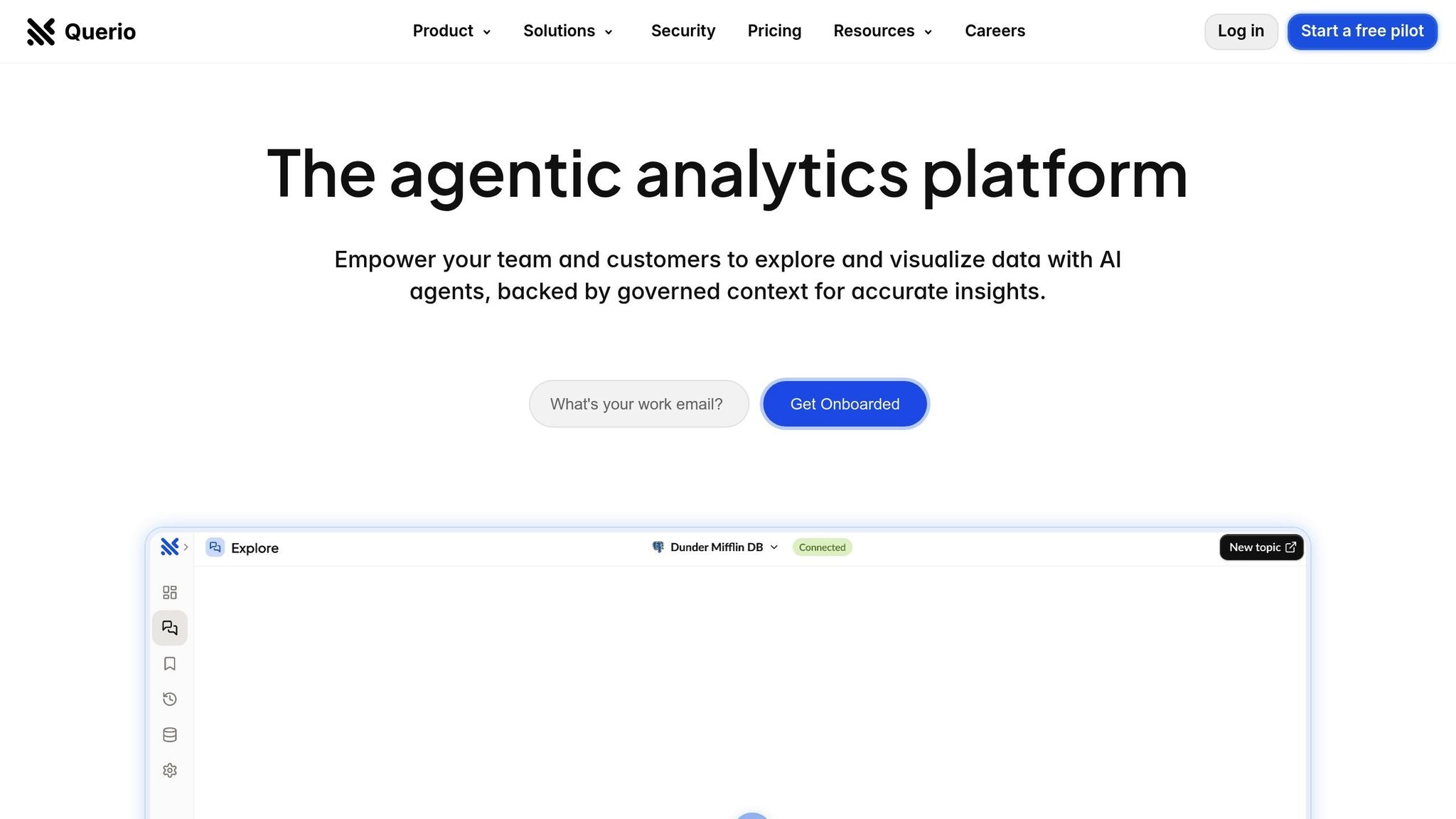
Querio uses a semantic layer to power natural-language queries, Python notebooks, and dashboards, ensuring all teams work with the same reliable data. This makes analytics accessible to everyone while maintaining governance and accuracy.
In short, a semantic layer transforms how SaaS teams use data, ensuring clarity, consistency, and efficiency across the board.
How a Semantic Layer Works: 3-Step Process for SaaS Data Management
Understanding the Semantic Layer in AI-Driven Data Analytics [GoodTalks]
What Makes Up a Semantic Layer
To make AI-driven analytics possible, a semantic layer relies on three core elements: precise data mapping, strict governance, and efficient query performance.
Business Entities, Metrics, and Relationships
At the foundation of a semantic layer are key business entities like customers, subscriptions, accounts, and products. These entities are mapped to raw data tables, and relationships between them are defined. This creates a structure that connects the dots across your data.
Metrics and KPIs are central to this setup. Instead of different teams calculating metrics like "monthly recurring revenue" or "customer churn rate" in their own ways, the semantic layer defines these calculations once. It ensures consistency across the board, even when dealing with complexities like non-standard calendars, fiscal periods, or currency conversions.
The real power comes from linking datasets effectively. By mapping entities to raw data and setting up relationships, the semantic layer can automatically join related tables for accurate queries. With entities and metrics clearly established, the focus shifts to securing and optimizing data access.
Governance and Security
A well-designed semantic layer organizes and secures your data. Row-level security ensures that users only see the data they’re authorized to access - sales managers view only their team’s accounts, while executives can see everything. Column-level masking further protects sensitive information, like hiding customer email addresses from users who don’t need to see them.
Role-based access controls integrate seamlessly with corporate directory services like Active Directory, LDAP, or Okta. This ensures consistent security policies, whether the data is being accessed via dashboards, AI tools, or Python scripts. Every interaction with the data is audited, keeping compliance in check.
"Defining metrics in MetricFlow is crucial for a unified source of truth. However, BI and AI tools often interpret metrics in their own ways. By leveraging open-source MetricFlow and other semantic tools, OSI can ensure every tool is consistent in the consumption of metrics. This saves analysts time, streamlines audits, and gives users the flexibility to access data as they prefer, without constant code updates." - Rob Vicker, Data Analytics Architecture Director, EMC Insurance
Query Optimization and Performance
Governance is just one part of the equation; speed and performance are equally important. The semantic layer translates user-friendly queries into efficient SQL that runs quickly on your data warehouse. Caching plays a big role here, storing results from frequently run queries so that users can get answers in under two seconds instead of waiting for the database to process everything again.
Pre-aggregation takes things a step further by automatically creating summarized versions of your data. For example, if monthly revenue trends are a popular query, the semantic layer will maintain aggregated tables to make those queries lightning-fast. This happens behind the scenes, requiring no extra effort from users.
All these optimizations occur without moving or duplicating data. The semantic layer works with your existing data platform, leveraging its computing power while handling query translation and acceleration.
Why SaaS Teams Need a Semantic Layer
SaaS companies often grapple with a familiar challenge: teams define critical metrics differently. For instance, the Product team might calculate "active users" one way, while the Finance team uses another method. Similarly, "churn" might carry varying meanings depending on the department. These inconsistencies can spark debates over which version of the data is correct, eroding trust and slowing down decisions across the organization. A semantic layer bridges the gap between technical and business perspectives, ensuring smoother decision-making for every team. By addressing these issues, a semantic layer delivers three key advantages: consistent metrics, easier access to data for non-technical users, and more reliable AI-driven insights.
Keeping Metrics Consistent Across Teams
When teams rely on separate logic to calculate important metrics, analytics tools can produce conflicting results. A semantic layer solves this by centralizing and standardizing metric definitions as part of a modern SaaS analytics tech stack. It acts as a bridge between business and data teams, ensuring calculations for metrics like "customer lifetime value" or "net revenue retention" are consistent across tools and reports. This means everyone, from marketing to finance, works with the same numbers and context, no matter where the data is accessed.
Empowering Non-Technical Users with Self-Serve Analytics
Product managers and finance analysts shouldn’t have to write complex SQL queries or wait on data teams to get simple answers. A semantic layer removes these bottlenecks by automatically translating business queries into secure, accurate data requests. For example, if a RevOps manager wants to see "Q4 expansion revenue by region", the semantic layer handles the heavy lifting - no SQL expertise or data team intervention required. Plus, it ensures that even self-service analytics align with governance rules and standardized metric definitions, keeping everything consistent and secure.
Reliable AI Insights and Automation
AI tools for self-serve analytics, from natural-language queries to predictive models, become far more effective when backed by a semantic layer. Without it, AI tools risk misinterpreting metrics or producing inconsistent results. A semantic layer provides pre-validated business logic, ensuring uniform metric interpretation across all AI-generated insights. Whether it’s automated reports or predictive analytics, querying data through a semantic layer guarantees the same level of accuracy and adherence to governance standards as manually created analyses. This makes AI tools not just smarter, but also more dependable.
How to Implement a Semantic Layer for SaaS Analytics
Adding a semantic layer to your SaaS analytics setup introduces a layer of translation and governance to your existing architecture. Here's a step-by-step guide to centralizing metric definitions, connecting your data warehouse, and enforcing security policies.
Define Metrics and Business Logic
Start by identifying the key metrics that drive your SaaS business - such as monthly recurring revenue (MRR), churn rate, customer lifetime value (LTV), and net revenue retention (NRR). Clearly document how each metric should be calculated, including specific filters, aggregation rules, and time frames. For example, decide whether an "active user" is defined by a single login or a meaningful action, and specify what constitutes "churn."
Bring together key stakeholders from different teams to ensure everyone agrees on these definitions. Tools like dbt’s MetricFlow can help codify these metrics in YAML, reducing redundant SQL and maintaining consistency across dashboards and AI-generated reports.
Connect to Data Sources and Build Models
Next, take stock of your main data sources - such as Snowflake, BigQuery, and Postgres - and pinpoint the core entities that drive your business, like subscriptions, users, events, invoices, and support tickets. Your semantic layer needs to understand how these entities relate to one another.
For instance, tools like Querio can seamlessly manage these connections, ensuring accurate and efficient joins between data sets. Define relationships, such as how a subscription links to a user or how event data ties into revenue metrics. Querio connects directly to your data warehouse using read-only, encrypted credentials, so there’s no need to copy data. This setup ensures that when someone asks, “What’s our expansion revenue by region for Q4?”, the semantic layer pulls from the correct tables and combines the data accurately.
Set Up Governance and Validate Iteratively
Governance is crucial for a reliable semantic layer. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to manage who sees what - for example, giving Finance access to detailed revenue data while limiting Customer Success to account health metrics. Use column-level masking to safeguard sensitive information like email addresses and payment details. Integration with identity management systems like Okta ensures that access policies align with your corporate directory.
Once governance rules are in place, validate them by having stakeholders run key reports and compare the results to existing dashboards. If discrepancies arise, trace them back to the metric definitions and make adjustments immediately. This iterative process builds trust in the system, encouraging teams to adopt the semantic layer over manual workflows.
How Querio Powers AI-Driven SaaS Analytics with a Semantic Layer
Querio is an AI-native business intelligence platform designed to streamline access to live data. By connecting directly to databases like Snowflake, BigQuery, and Postgres through read-only credentials, it allows teams across departments - from Product to Finance - to ask questions in plain English and get accurate, visual answers in seconds. This approach simplifies the process of uncovering actionable insights, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Natural-Language Queries and AI Workspaces
Querio uses AI-powered natural-language querying to make data exploration easier. For example, a product manager can type a query like, "What's our MRR growth by region for Q4 2025?" and instantly receive a detailed chart. These visualizations are built on consistent metric definitions, ensuring everyone works with the same reliable data - no more conflicting numbers or interpretations across teams.
Self-Serve Dashboards and Embedded Analytics
With Querio, teams can create intuitive dashboards to monitor KPIs and share insights effectively. Once a dashboard is built, it’s easy to automate reports for executives or embed analytics into customer-facing apps. This embedded feature ensures a seamless experience for end users, while unlimited viewer access means everyone stays informed without additional costs.
Python Notebooks for Advanced Analysis
For those who need deeper data exploration, Querio includes a Python notebook environment. Analysts can combine SQL and Python in this workspace, all while maintaining consistent metric definitions and governance. This reduces the chance of errors or inconsistencies in reporting, making advanced analysis both powerful and reliable.
Conclusion: The Role of Semantic Layers in SaaS
A semantic layer simplifies SaaS data management by aligning metric definitions across the board, ensuring consistency and trust in decision-making. When teams - from Product to Finance - operate with the same business logic, disagreements over conflicting numbers become a thing of the past.
It also gives non-technical users the ability to explore data independently, speeding up the discovery of insights while allowing technical teams to focus on high-priority projects. This self-service model removes bottlenecks, enabling teams to act on insights without delay.
By connecting raw data with business logic, a semantic layer also supports AI-driven analytics, producing outputs that are not only actionable but also traceable and easy to understand. This structure is critical for SaaS companies aiming to automate decisions and expand their analytics capabilities efficiently.
Querio demonstrates the benefits of a semantic layer by directly linking to live data, creating governed dashboards, and enabling advanced analysis with consistent definitions. These features streamline workflows, enhance data security, and ensure accuracy - reinforcing the earlier points about reliable metrics, secure processes, and optimized query performance.
FAQs
How does a semantic layer enhance data consistency for SaaS companies?
A semantic layer serves as a centralized source of truth, bringing consistency to business metrics and logic across various tools and applications. By providing unified definitions of data, it breaks down silos and reduces the chances of misinterpretation.
This consistency allows SaaS companies to make decisions more effectively. Both technical and non-technical teams can access dependable insights quickly, improving workflows, cutting down on errors, and ensuring data stays aligned with business objectives.
How does a semantic layer improve AI-driven insights in SaaS platforms?
A semantic layer takes the complexity out of raw data by translating technical structures into everyday business terms like Revenue, Customer Churn, or Active Users. Think of it as a bridge that creates a clear, unified view of your data, making it easier for both analysts and AI systems to interpret - without requiring anyone to write SQL or wrestle with technical intricacies.
By embedding consistent definitions and calculations, the semantic layer ensures that AI-generated insights - whether they come from dashboards, AI copilots, or automated reports - align perfectly with your organization’s goals and business rules. This not only reduces errors but also builds trust in AI-driven analytics, making insights more practical and accessible for everyone, from data experts to business teams.
How does a semantic layer make SaaS analytics easier for non-technical users?
A semantic layer makes SaaS analytics easier by turning complex technical data into straightforward, business-friendly terms like revenue, customer churn, or active users. It simplifies the process by hiding the intricate data architecture, meaning non-technical users don’t have to write SQL queries or deal with confusing technical language. Instead, they can focus on what really matters - asking key business questions and getting insights quickly.
With this layer in place, business users can effortlessly create self-serve dashboards, generate reports, or leverage AI-driven tools using plain-language prompts. By standardizing definitions and enforcing security measures, it ensures everyone is working with the same accurate information. This not only reduces errors but also boosts confidence in the data, enabling faster and more dependable decision-making across the organization.

