
How to Add Natural-Language Analytics to Your Product
Business Intelligence
Dec 20, 2025
Step-by-step guide to add natural-language analytics: plan personas, build a semantic layer, convert plain-English queries to accurate visuals, embed securely, and iterate.

Natural-language analytics (NLA) lets users ask data questions in plain English and get instant, visual answers - no technical skills required. This approach eliminates delays, reduces analyst backlogs by up to 80%, and saves users 7–10 hours weekly. Here's how to integrate NLA into your product:
Understand User Needs: Identify key user personas (e.g., sales managers, product managers) and document their common workflows and queries.
Set Up Your Data: Connect to a centralized data warehouse (e.g., Snowflake, BigQuery) and create a semantic layer that translates technical data into business-friendly terms.
Build the Query Experience: Use AI to transform plain-English questions into database queries and return results as charts or tables. Add user-friendly features like clarification prompts and visualizations.
Embed Analytics: Integrate NLA directly into your product with secure authentication, responsive design, and customizable themes.
Add Guardrails: Implement input/output checks to prevent errors or security risks, and monitor system performance to refine over time.
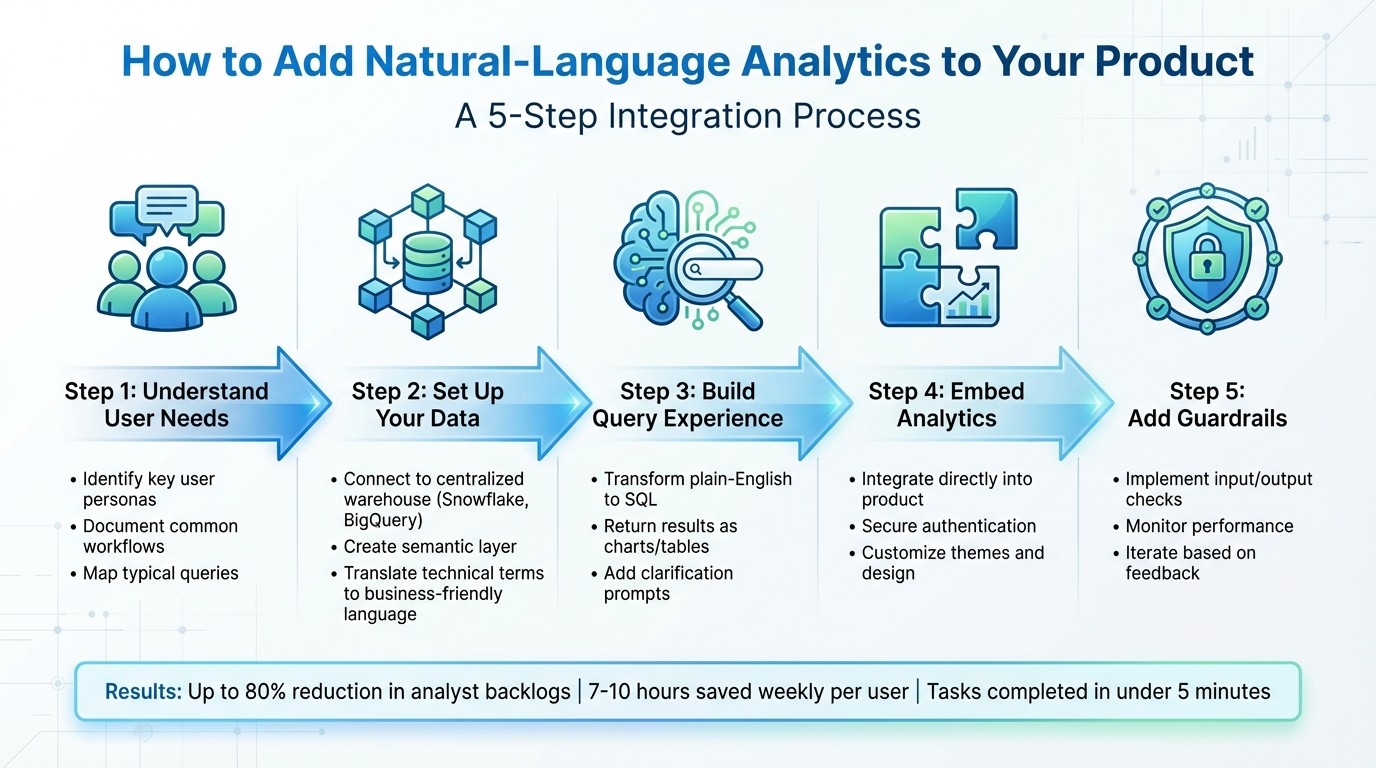
5-Step Process to Integrate Natural-Language Analytics into Your Product
Integrating Serverless LLMs with Data Platforms for Natural Language Analytics - Kamesh Sampath
Planning Your Natural-Language Analytics Integration
To ensure your natural-language analytics (NLA) system becomes an indispensable tool rather than a forgotten feature, start by understanding the roles of your users and the kinds of questions they need answered. This foundational planning sets the stage for success.
Identify Core User Personas and Needs
Begin by defining personas for each user group. For example, a sales manager might focus on pipeline metrics and conversion rates, while a product manager prioritizes feature adoption and user retention. These personas reflect real individuals with specific workflows, challenges, and varying levels of technical expertise.
Take a deep dive into current workflows to uncover bottlenecks. For instance, if your marketing team spends hours manually compiling campaign performance data, that's a clear opportunity for improvement. Determine which tasks are better suited for automation - like generating routine reports - and which require human input, such as nuanced budget forecasting. For example, while a finance team might welcome automated reporting, they may prefer human-augmented analysis for strategic decisions.
Once you’ve pinpointed user needs, document their typical queries and processes. This clarity ensures your system is tailored to their real-world challenges.
Define Use Cases and Workflows
With user personas in hand, map out the specific questions they’ll ask. Your NLA should handle common analytical patterns like:
Aggregations: "What’s the total revenue?"
Grouping: "Show sales by region."
Filtering: "Only include Q4 data."
Sorting: "Top 10 customers by spend."
These patterns provide a framework for addressing real business questions effectively.
Next, create a set of "golden queries" that reflect your organization’s specific business logic. For instance, if your company defines "active users" as those who’ve logged in within the past 30 days, document that explicitly. Similarly, if "revenue" calculations exclude refunds and taxes, make that definition clear. These golden queries help train the AI to align with your unique business operations rather than generic data warehouse logic. You can also set persona-specific defaults - like summing revenue for a sales dashboard or averaging test scores for an education product.
Set Success Metrics
To measure the success of your NLA implementation, establish clear metrics. Frank te Pas, Head of Product at Enterprise, highlights this approach:
The most important metrics are specific to your goals. For us, these include if our customers are successful with this product, are we driving value... How much faster can customers go through their workflows? How much time do they save?
Select metrics that align with your objectives, such as improving workflow speed or reducing time spent per task. For early stages, focus on Time to First Value (how quickly users get their first meaningful result) and Goal Completion Rate (the percentage of queries that return useful answers). As your system matures, track metrics like Customer Expansion Rate (how many additional teams adopt the tool) and Product Usage Diversity (the range of questions being asked). Monitoring support tickets per active user can also highlight areas of confusion or friction.
Finally, define a North Star Metric that captures the long-term value of your system. This could be something like "queries answered per user per week" or "hours saved per department per month." Share this metric with your team to keep everyone aligned and focused on the bigger picture.
Preparing Your Data and Semantic Layer
To enable users to ask questions in plain English, your data needs to be presented in terms that are easy for business users to understand. This involves connecting to a dependable data source, translating technical database structures into relatable business concepts, and setting up rules to ensure accuracy and security. A solid foundation starts with consolidating your data in a centralized warehouse.
Connect to a Centralized Data Warehouse
Begin by connecting to a cloud-based data warehouse like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres. Centralizing your data ensures consistent answers and avoids discrepancies across your platform. Use a dedicated service account with limited permissions specifically for your analytics layer to maintain security. Many warehouses offer features like "Partner Connect", which simplify setup and reduce configuration time significantly - what used to take hours can now be done in minutes. For instance, when setting up Snowflake, factor in potential token-based costs during your infrastructure planning. To handle time-based queries effectively, configure a time spine model that supports daily, weekly, and monthly granularities, enabling precise rolling window calculations.
Design a Semantic Layer for Business Context
The semantic layer is where raw database structures are translated into terms that make sense to your users. Map technical fields to business-friendly names, and enhance clarity by including synonyms, descriptions, and example values. Define relationships between tables, such as connecting a CUSTOMER table to an ORDERS table with a many-to-one relationship, and specify join types. These mappings create a bridge between technical data and everyday business language, ensuring consistent query results. Erik George, Solutions Architect at dbt Labs, highlights the importance of this approach:
The accuracy component is the very unique value proposition... we're not asking the LLM to write a SQL query, which is prone to hallucinating... instead, it generates a highly structured MetricFlow request.
Start small - use 3–5 tables and 10–20 columns initially - then expand as you confirm accuracy and gather feedback from users.
Enforce Data Quality and Governance
Clear standards are essential to avoid inconsistent or misleading results in natural-language analytics. Document your schema thoroughly, using detailed metadata to explain how technical structures relate to business concepts. For example, describe what each table represents, define calculations, and specify the types of values in each field. Create a Verified Query Repository (VQR) - a collection of pre-approved questions and their SQL translations. These serve as examples to guide the AI, especially for complex business logic like "Active customers are those who've made a purchase in the last 90 days."
Implement access controls that comply with your organization’s data security policies, ensuring users only see what they’re authorized to view. Capture key business calculations directly in the semantic layer using expressions like "Profit = Revenue - COGS." This eliminates the need for the AI to derive these formulas, reducing errors and speeding up responses. This structured approach supports Querio’s mission to provide reliable, AI-driven insights seamlessly integrated into your product.
Building the Natural-Language Query Experience
Once you’ve set up your data and semantic layer, the next step is crafting an interface that allows the AI to interpret questions accurately and present results in a way that’s easy for business users to understand. This involves creating a pipeline that connects user input to your database, enables the AI to process queries, and displays the answers in a clear, actionable format.
Implementing a Natural-Language-to-Query (NLQ) Pipeline
The NLQ pipeline is what transforms plain-English questions into structured database queries. Here’s how it works: user input is passed to a large language model (LLM) via LangChain. The LLM then translates the question into SQL, runs it against your data warehouse, and returns the results. To make this process work seamlessly, the LLM needs to be grounded in a context layer that includes schema metadata, business logic, and domain-specific terms.
For example, you can use a value index to map natural language phrases - like “Hoodie” or “luxury product” - to specific database columns and values, ensuring the AI filters the right fields. For commonly asked or complex questions, it’s helpful to store curated question-query pairs. For instance, you might save “What were sales last quarter?” along with its optimized SQL query to ensure consistent and reliable responses.
To further guide the LLM, annotate schemas with native types such as TypeScript interfaces or Pydantic models. Include 2-3 sample documents in the prompt to give the LLM a clear understanding of your data structure. This setup creates a strong foundation for enriching prompts and delivering accurate outputs.
Designing LLM Prompting and Context Enrichment
For effective LLM orchestration, prompts need to be enriched with detailed schema metadata. The LangChain team underscores the importance of this:
The semantic layer plays a key role in ensuring correctness and predictability when building text-to-sql LLM-based applications.
Your prompts should include table comments, column descriptions, and relationship definitions. Use step-by-step instructions to guide the LLM through selecting relevant tables, operators, and transformations before generating code. For more complex queries, break them into smaller subtasks using task decomposition, which improves accuracy, especially with large datasets.
Ambiguity is a common challenge - about 20% of user queries fall into this category, with 55% being unclear and 45% unanswerable. Instead of guessing, implement clarification prompts that ask users for more details. To maintain security, execute AI-generated queries against parameterized secure views, which ensure fine-grained access control and prevent unauthorized data exposure. Once the queries are accurate, the focus shifts to presenting the results in a user-friendly way.
Presenting Results with Clear Visualizations
After the query runs, the results need to be displayed in formats that align with how users make decisions. Whether it’s tables, charts, or narrative summaries, the presentation should follow US conventions, such as using commas for thousand separators, MM/DD/YYYY for dates, and USD for currency.
To build trust in the AI’s output, include a confidence score with the results, so users can gauge when additional verification might be needed. For deeper insights, add explainability metrics like SHAP values to help users understand how the AI arrived at its conclusions.
As Alation puts it:
The future of data interaction is conversational, accessible, and increasingly powerful - and that future is arriving now.
Frameworks like LangChain or Streamlit can help bridge the gap between SQL query results and user-facing visualizations. Ensure these visualizations are linked to your data catalog, so users can easily understand the metrics behind the numbers.
Embedding Analytics into Your Product
Once you've built your NLQ (natural-language query) pipeline, the next step is embedding analytics directly into your product. This integration ensures that analytics feel like a natural extension of your platform, maintaining a seamless user experience that aligns with your brand's design and functionality.
Choose the Right Embedding Patterns
There are a few ways to incorporate natural-language analytics into your product, depending on how your users interact with data:
A standalone search bar is perfect for quick, on-the-spot answers without disrupting the current screen. Think of it as a command palette for data.
A conversational sidebar allows users to ask follow-up questions while staying within their workflow.
A full-page "Generative Q&A" experience is ideal for more complex queries, offering space for users to explore, iterate, and compare multiple visualizations side by side.
Pick the approach that aligns best with your users' needs - whether they require quick insights, contextual follow-ups, or deep dives into their data.
Technical Steps for Embedding Analytics
Successfully embedding analytics involves a combination of backend and frontend coordination. Here’s how to do it:
Secure Authentication: Use IAM roles or JWT to authenticate users before generating a signed, time-limited URL via an API like
GenerateEmbedUrlForRegisteredUser. These URLs typically expire within 5 minutes, but sessions can last up to 10 hours.Frontend Implementation: Leverage a JavaScript SDK or Web Components to manage responsive layouts, apply custom themes (using parameters like
themeIdor CSS variables), handle event callbacks, and enforce multi-tenant security through Row-Level Security (RLS).Domain Authorization: Ensure your product’s domain is added to the analytics provider’s allow list (CORS settings). Most platforms support up to 100 static domains, and some even allow dynamic subdomain authorization through API parameters.
By following these steps, you can create a secure, customized analytics experience that feels fully integrated into your product.
Use Querio's Embedded Analytics Features
Querio makes it easy to embed natural-language querying and dashboards directly into your SaaS platform. Its semantic layer ensures users receive accurate answers without needing to understand the complexities of your data structure.
With Querio, you can enable topic selection for products that span multiple data domains, such as Sales and Inventory, letting users switch datasets seamlessly. The conversational text box simplifies data exploration, especially for non-technical users. Best of all, Querio doesn’t charge hidden query fees, so you can offer unlimited analytics access without worrying about unexpected costs as your user base grows.
Implementing Guardrails and Iterating on NLA
Once your NLA is deployed, it’s crucial to secure, refine, and monitor it to prevent issues like data leaks, inaccuracies, or delays. These steps will help keep your system reliable and responsive over time.
Add Data Security and Query Guardrails
Guardrails provide essential layers of protection for your system. Input guardrails intercept harmful prompts - like attempts to override system instructions or inject unauthorized commands - before they’re processed. Output guardrails, on the other hand, review generated responses for issues like hallucinations, sensitive information (PII), or irrelevant answers before they reach the user.
For straightforward tasks such as detecting PII or banned terms, use deterministic rules like regex patterns or keyword blocklists. However, for more complex challenges - such as identifying bias or verifying facts - model-based guardrails can be employed, using an LLM-as-a-judge approach. But keep in mind, stacking multiple guardrails can increase false positives if not calibrated properly. For instance, with five guardrails at 90% accuracy each, the false positive rate could climb to 40%.
"Consider the LLM to be, in effect, a web browser under the complete control of the user, and all content it generates is untrusted."
– NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails
Always treat LLM-generated content as untrusted. Avoid allowing the system to execute raw SQL directly. Instead, extract parameters from the LLM and inject them into pre-audited, hard-coded templates. For sensitive actions, like deleting records or sending emails, require explicit human approval before execution. If a query is blocked, handle it gracefully by showing a generic error message without exposing internal database structures or API details.
Monitor and Log User Interactions
To improve your system, you need to measure its performance. Log every query, from the original user input to the final formatted result, along with details like API parsing and authorization context. This comprehensive tracking - often called AI tracing - gives you a clear view of how each response is generated.
Key metrics to monitor include semantic similarity (does the response align with user intent?), latency (are responses timely?), and refusal ratio (how often are requests denied?). A spike in refusals could indicate either attempted security breaches or overly cautious settings. Companies that prioritize AI observability have reported up to an 80% reduction in downtime and a 90% improvement in resolving issues, which translates to substantial cost savings.
Frameworks like OpenTelemetry can help capture telemetry data for every step in the query process, including model version, duration, and token usage. This level of visibility not only simplifies debugging but also builds user trust by offering transparency into how queries are processed.
Use the insights from your logs to fine-tune guardrails and improve your semantic layer.
Iterate Based on Feedback
Your semantic layer should evolve as users interact with the system. Over time, you’ll uncover new ways users phrase their questions, additional terms they expect the system to recognize, and edge cases where accuracy might falter. For example, you can enhance the system by adding synonyms (e.g., linking "revenue" and "sales" to the same metric), refining business definitions, and building a library of golden queries - verified natural-language-to-SQL pairs that reflect your organization’s logic.
Leverage intent mining to analyze past conversations and identify common phrasing patterns. If users frequently ask about "last quarter's performance" and the system doesn’t recognize it, update the semantic layer to address this gap. You can also present saved queries as pre-built templates in your UI, allowing users to start with reliable options rather than crafting queries from scratch.
When adjusting guardrails, strike a balance. Settings that are too strict may block valid queries, frustrating users and slowing down workflows. Monitor guardrail performance closely and adjust thresholds based on real-world usage. For systems that require real-time responses, configure the LLM-as-a-judge to return binary (0 or 1) flags instead of continuous scores. This reduces processing time and keeps latency low.
"Building a solid foundation of guardrails ensures that your LLM doesn't just perform well on paper but thrives safely and effectively in the hands of your users."
– Jeffrey Ip, Cofounder, Confident AI
Conclusion
By following the steps in this guide - from planning your integration and preparing your AI semantic layer to building a user-friendly query experience and setting up guardrails - you can turn what used to take days of manual analysis into just minutes. With an AI-powered system, tasks that once required significant time can now be completed in under five minutes.
Think of NLA as a system that evolves over time, not a one-and-done implementation. As discussed earlier, refining your semantic layer and guardrails is key to its growth. Over time, your semantic layer becomes smarter as you add synonyms and refine business definitions, while your guardrails strike a better balance between security and usability. This gradual evolution helps users transition from relying on static dashboards to confidently exploring data through conversational, ad-hoc queries. Tools like Querio make this process seamless, simplifying everything from querying data to creating visualizations.
"What used to be a week-long process now takes minutes." – Jennifer Leidich, Co-Founder & CEO, Mercury
Querio takes this approach even further by integrating directly with data warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres, removing the need for complex ETL pipelines. Its embedded analytics features allow you to align with your product's design system, while its semantic layer ensures that every query carries the right business context. This means non-technical users can ask detailed questions in plain English and receive accurate, visual answers in seconds - all while the data team maintains oversight.
"It's not just about saving time and money, it's about making data accessible." – Enver Melih Sorkun, Co-founder & CTO, Growdash
The future of analytics is shifting from traditional click-to-filter methods to intuitive, prompt-driven experiences. By adopting NLA today, you're not just keeping up with trends - you’re empowering users to make quicker, smarter decisions without needing to wait for analysts or learn SQL. These steps pave the way for faster insights and a smoother, more accessible analytics experience.
FAQs
How can I make sure my natural-language analytics system meets my business goals?
To make sure your natural-language analytics (NLA) system supports your business goals, start by clearly outlining what you want to achieve. Identify the key metrics that matter most to your team and stakeholders. Then, translate these objectives into a semantic layer - a structure that organizes raw data into easy-to-understand, business-relevant terms. This step ensures everyone in your organization works with consistent and clear data.
Next, prioritize data quality and governance. Clean and standardize your data to reduce errors and avoid confusion. Set up strong controls to manage who can access the system, enforce security measures, and track how the system is used. These steps are essential for building a reliable and secure NLA system that can scale with your business.
Finally, bring end-users into the process early. Gather their feedback on how the system handles queries and delivers results. Use this input to fine-tune the language model so it better understands your business’s specific terminology and decision-making processes. By continuously refining the system based on real-world usage, you'll develop an NLA solution that fits seamlessly into your business intelligence strategy and delivers insights that truly drive action.
What are the best practices for ensuring data security in natural-language analytics?
To maintain robust data security while integrating natural-language analytics (NLA) into your product, start by using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls. These measures help ensure that only authorized users can access or interact with sensitive information.
You should also encrypt all data - both at rest and in transit - using well-established industry protocols. Treat every interaction with the model, including prompts and responses, as sensitive data to guard against unauthorized access. For added protection, implement data masking or anonymization techniques to safeguard personally identifiable information before it reaches the language model.
Lastly, prioritize continuous monitoring and keep detailed audit logs of all NLA-related activities. Regularly evaluate and update your security practices to address emerging threats and stay aligned with changing regulations.
How can I evaluate the success of adding natural-language analytics to my product?
To evaluate how well your natural-language analytics (NLA) system is performing, focus on two key areas: user impact and technical performance.
For user impact, track metrics like:
Time-to-insight: How quickly users can find answers compared to older, more traditional methods.
Adoption rate: The percentage of users actively using natural-language queries.
Query-success rate: How often questions are answered correctly on the first try.
User satisfaction: Use short surveys to understand how users feel about their experience.
When it comes to technical performance, keep an eye on natural language processing (NLP) metrics such as:
Accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score: These ensure the system is interpreting queries correctly.
For more advanced scenarios, metrics like BLEU and ROUGE can help evaluate the quality of generated responses.
Regularly reviewing these indicators will help you pinpoint areas for improvement and ensure the system continues to meet user expectations.
Lastly, tie these metrics back to business outcomes. For example, look at engagement rates (like follow-up actions or additional queries) and AI visibility (how often NLA results influence decision-making). A combination of high adoption, satisfied users, and accurate results shows that your NLA system is delivering real value.

