Best Practices for Role-Based Security in BI Platforms
Business Intelligence
May 31, 2025
Learn effective strategies for implementing role-based security in BI platforms, ensuring data protection and compliance with regulations.

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is essential for securing Business Intelligence (BI) platforms. It ensures users only access the data they need for their roles, reducing security risks and meeting compliance requirements like GDPR and HIPAA. Here's what you need to know:
Key Benefits of RBAC:
Simplifies access management by grouping users into roles.
Enforces the principle of least privilege to minimize risks.
Scales easily as organizations grow or roles change.
Helps meet regulatory compliance with transparent access controls.
Implementation Steps:
Conduct a permissions audit to identify vulnerabilities.
Define clear roles based on organizational workflows.
Automate role management to reduce errors and save time.
Use advanced features like row-level security and column-level security for precise control.
Ongoing Maintenance:
Regularly review and update access permissions to prevent "permission creep."
Monitor activity logs and set up alerts for suspicious behavior.
Remove unused roles to reduce security risks.
RBAC is critical for protecting sensitive data in BI platforms while maintaining operational efficiency. By following these best practices, you can build a scalable, secure, and compliant access control system.
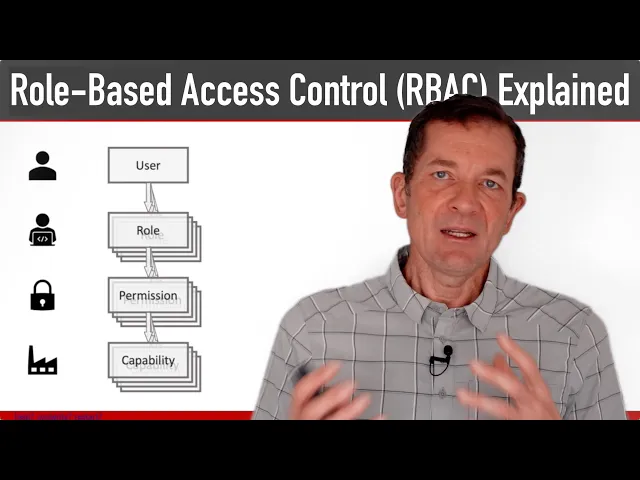
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) Explained: How it works and when to use it
Core Principles of Role-Based Security
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is built around three key components: users, roles, and permissions. Users are the individuals requiring access to business intelligence (BI) systems, roles define sets of permissions tied to specific job responsibilities, and permissions determine the actions users are allowed to take on various resources.
RBAC operates on a structured approach where administrators define roles based on organizational responsibilities and assign users to those roles. This setup not only simplifies management but also strengthens security by ensuring access is tightly controlled.
A cornerstone of RBAC is the principle of least privilege, which ensures users only have the permissions needed to perform their job functions. This approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and reduces the organization's attack surface [2]. When implemented properly, this principle provides robust layers of security without compromising productivity.
One of RBAC's standout features is its ability to scale and adapt as organizations grow. When new employees join, they can quickly be assigned to predefined roles, and any updates to roles automatically apply to all associated users. This flexibility makes RBAC a practical choice for evolving organizational needs, as detailed in the next section on role and permission setup.
Setting Up Roles and Permissions
Creating effective roles begins with aligning them to the organization’s structure and specific data access needs. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) outlines three basic rules for RBAC systems: role assignment, role authorization, and permission authorization [3].
To start, categorize users into three broad groups:
Administrators: Require full access for system maintenance and configuration.
Specialists or expert users: Need advanced analytical tools and broader data access relevant to their expertise.
End users: Typically need view-only access to specific reports and dashboards tied to their daily tasks.
For example, a hospital implementing RBAC might create a "Nurse" role. This role could include permissions to view medication details and update electronic health records. Nurses logging into the system would only have access to these specific functions, while actions like prescribing medications or ordering tests would remain restricted to physicians [3].
Hierarchical role structures often mirror organizational charts. Managers might have full permissions, while their team members receive subsets of those permissions. Users can also be assigned multiple roles or grouped into role collections, allowing for nuanced access controls. Roles can be tailored to job titles or specific conditions, ensuring precise and effective access management [3].
Preventing Permission Creep
Permission creep, also known as privilege sprawl, occurs when users accumulate unnecessary access rights over time [4]. This can happen when employees retain permissions from previous roles or gain additional access without proper oversight, creating significant security vulnerabilities.
Given that over 2,200 cyberattacks occur daily - roughly one every 39 seconds - addressing permission creep is critical for safeguarding organizational data [4].
Regular access audits are essential for combating permission creep. These audits compare user permissions with current job responsibilities to identify and revoke unnecessary access rights [4][5]. Automating these reviews can reduce administrative workload and improve accuracy. Additionally, Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) systems can enforce strict access policies while maintaining detailed audit trails [5]. A good starting point is to grant minimal permissions and add access only when necessary.
By addressing permission creep, organizations can maintain a secure and efficient RBAC system, which is further strengthened by aligning security models to business workflows.
Matching Security Models to Business Requirements
For RBAC to be effective, security controls must align with the organization’s workflows. Striking the right balance between security and operational efficiency ensures that access controls support, rather than hinder, daily business processes.
Compliance requirements often shape security models. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX demand specific access controls and audit capabilities, which RBAC is well-suited to handle. Conducting a detailed analysis of business workflows can help identify logical role boundaries and the necessary permissions. This process often uncovers opportunities to streamline access while maintaining robust security.
Phased rollouts can help ease the transition during RBAC implementation [2]. Training users on the system’s purpose and functionality is equally important to ensure smooth adoption.
For BI platforms like Querio, where users interact with data through natural language queries and AI tools, RBAC becomes even more critical. Permissions must account for not only the data users can access but also the ways they interact with it - whether through dashboards, reports, or advanced analytics. This is a core component of natural language BI systems. This requires sophisticated permission models that apply consistent security policies across all interaction methods.
Regular policy reviews are vital to ensuring RBAC systems continue to meet both business and security needs. As organizations grow and evolve, periodic assessments can confirm that roles and permissions remain aligned with current objectives, reinforcing the security of BI platforms through systematic best practices.
Implementation Best Practices for Role-Based Security
Putting role-based access control (RBAC) into action within your BI platforms takes a structured approach. It’s about identifying security gaps, defining clear role structures and automated processes, to keep things manageable as your organization grows. Let’s break it down.
Running a Permissions Audit
The first step is understanding who has access to what. A detailed permissions audit helps uncover vulnerabilities and ensures that access rights align with actual needs.
Start by listing all user accounts in your BI platform, including both active and inactive ones. Dormant accounts often retain unnecessary permissions, posing a security risk. Pay close attention to users who have accumulated access beyond what their current roles require.
During the audit, focus on key areas like access patterns, the sensitivity of the data, and compliance requirements. For instance, review login logs to spot inactive accounts and categorize your data by sensitivity - ensuring that sensitive information, such as financial records or personal customer data, is properly secured.
Don’t forget to check service-level and row-level security configurations to ensure they match current job responsibilities [6]. Document these findings thoroughly. This baseline will guide your new RBAC structure and provide a solid case for any changes you propose.
Creating Detailed Role Structures
Designing a role hierarchy that balances precise access control with ease of management is critical. Your roles should reflect your organization’s workflows while being adaptable to changes.
Start by aligning roles with your organizational structure. Consider creating functional roles that span across departments, like "Financial Analysts" or "Customer Data Viewers." This grouping allows you to manage access for users with similar needs more efficiently.
A hierarchical structure often works best for BI platforms. For example, a Regional Sales Manager might have access to all sales data for their region, while individual sales reps only see data tied to their specific accounts.
Leverage your BI platform’s tools - like Power BI Desktop’s "Manage Roles" feature - to define roles and apply security filters. Use DAX expressions to enforce dynamic filtering based on user attributes [6]. To keep things manageable, group similar roles together. Instead of creating separate roles for "Sales Manager – East Coast" and "Sales Manager – West Coast", opt for a single "Sales Manager" role with dynamic filters that adjust access based on the user’s location.
As your organization grows, manual role management can become overwhelming. That’s where automation comes in.
Setting Up Automated Role Management
Once your role structures are in place, automation helps scale RBAC smoothly and ensures consistency as your organization evolves. Managing roles manually becomes impractical over time, and automation reduces the risk of errors while streamlining administrative tasks.
Integrating your BI platform with HR systems is a game-changer. When employees are hired, change roles, or leave the organization, these updates should automatically reflect in your BI platform. Identity management solutions can synchronize user attributes across systems to make this happen seamlessly.
For example, in Microsoft environments, Azure Active Directory (AAD) supports dynamic membership rules. These rules automatically update security group memberships based on changes in user properties [8]. By mapping BI roles to these security groups, you can reduce the workload when employees switch teams.
Automate provisioning and deprovisioning to ensure that access is updated or removed as roles change. Scheduled access reviews can also help flag unusual access patterns, like accounts with excessive permissions or those that haven’t been used recently. While human oversight is still important, automation can prioritize and streamline these reviews.
For larger organizations, tools like Administration Web Services can automate tasks such as user creation, role assignments, and content access delegation [7]. This programmatic approach ensures that security policies are consistently applied and reduces the chance of manual errors.
Keep an eye on your automated systems. Set up alerts for failed synchronizations or unusual activity, so you can address potential issues quickly. Regular monitoring helps maintain the integrity of your RBAC model while cutting down on manual effort.
Advanced Security Features for BI Platforms
Modern BI platforms go beyond basic Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to include advanced security measures that protect sensitive data. These features build on the RBAC foundation and automated management practices to provide an extra layer of protection.
Row and Column Level Security
Traditional RBAC controls access to entire datasets, but row-level security (RLS) and column-level security (CLS) allow for more precise data control. RLS uses SQL filters to limit access to specific rows of data - for example, showing a physician only their own patients' records. CLS, on the other hand, restricts access to specific fields, such as limiting visibility of salary information to HR staff only. To add another layer of protection, dynamic data masking (DDM) can be used to obscure sensitive data values [9][10].
Setting Up Access Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time monitoring and automated alerts are critical for spotting potential security threats early. Regularly reviewing activity logs helps identify unusual behaviors, like access during odd hours or large-scale data downloads [11]. In Microsoft environments, tools such as Azure Active Directory, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, and Microsoft Sentinel work together to provide robust monitoring and alerting systems. These tools ensure that any suspicious activity triggers immediate notifications, allowing for a quick response [12][13]. It’s important to fine-tune alert settings to catch serious incidents without overwhelming administrators with too many notifications.
Using AI for Role Management
AI has taken automated role management to the next level by optimizing permissions in real time. It analyzes user behavior to recommend adjustments, detect misconfigurations, and enable just-in-time (JIT) access, which provides temporary permissions only when needed. For example, Querio leverages AI through natural language interfaces and intelligent agents to dynamically adjust roles based on user activity. This approach reduces permission creep and ensures that security settings stay aligned with business needs. A practical case in the transportation industry showed how AI-driven analytics improved operational visibility and streamlined workload management [14].
Long-Term Role-Based Security Maintenance
Maintaining role-based security isn’t a one-and-done task. It requires consistent effort to adapt to changing roles and business needs. Without proper upkeep, vulnerabilities can creep in, putting sensitive information at risk. Here’s how organizations can keep their access controls strong over time.
Conducting Regular Access Reviews
Periodic access reviews are the backbone of effective security. They ensure that user permissions stay aligned with current responsibilities and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Consider this: In November 2022, Meta was fined $277 million by Ireland's Data Protection Commission after the personal data of 500 million users was compromised. Similarly, in 2023, Tesla faced a data leak caused by former employees exposing personal information [15]. These incidents underscore the critical need for regular access reviews.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting effective reviews:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1. Establish a Review Policy | Define the scope, frequency, and key stakeholders for access reviews. |
2. Assign Data Owners | Identify individuals responsible for managing access to specific resources. |
3. Compile Access Information | Collect a detailed snapshot of current access permissions across systems. |
4. Review Access Rights | Ensure permissions align with each user’s current role. |
5. Document Outcomes & Adjust Access | Record findings and make necessary changes to access rights. |
Given the complexity of modern IT environments, automation plays a vital role in streamlining these processes. Cross-functional collaboration is equally important - teams from IT, security, HR, and legal should work together, with all reviewers regularly trained on updated policies and regulations.
Managing Permission Changes Over Time
Keeping an eye on real-time permission changes is just as important as scheduled reviews. Without continuous monitoring, gaps can emerge as roles and responsibilities shift, leaving systems vulnerable.
A stark example of this occurred in 2018 when British Airways suffered a cyberattack that exposed the personal and financial data of over 400,000 customers. This breach resulted in a £20 million fine from the Information Commissioner’s Office [16].
"While compliance definitely helps drive security, compliance does not equal security." – Verizon Data Breach Report [16]
To address this, organizations should use tools that track user activity, such as logins and access attempts, to quickly spot unauthorized changes. Applying the principle of least privilege - granting users access only to what’s necessary for their role - further strengthens security.
Removing Unused Roles
Unused roles are more than just clutter - they’re a security risk. Reducing the number of roles and limiting their scope minimizes the damage that could occur if a security breach happens.
A helpful development came in February 2024, when AWS introduced last-used timestamps for IAM roles. This feature helps administrators pinpoint and remove roles that are no longer active [17]. By analyzing access logs, teams can identify and eliminate outdated permissions with confidence.
Regularly cleaning up unused roles prevents "role explosion", where the sheer number of roles becomes unmanageable. During these audits, IT teams and business stakeholders should work together to ensure that removing a role won’t disrupt operations. All changes should be documented for future reference.
For BI platforms, maintaining security is an ongoing effort. At Querio, we’re dedicated to providing data teams with role-based security solutions that grow and adapt as businesses evolve.
Building Secure and Scalable BI Security
Creating a secure and scalable BI security framework involves more than just managing roles and conducting access reviews. It’s about aligning security measures with your organization's growth, ensuring both protection and operational flexibility. Below are key strategies to help you establish a strong foundation for scalable BI operations.
Start with your organizational chart when designing roles. By mapping roles directly to your organizational structure, you can ensure that data access naturally aligns with job responsibilities and reporting lines. This approach simplifies adjustments as your organization evolves [18].
"RBAC provides a scalable solution that can adapt to changing organizational structures and roles. Whether a company is expanding its workforce, adding new departments, or integrating new systems, RBAC can easily accommodate these changes without compromising security or efficiency."
The Grow Team [1]
Integrate your BI platform with trusted systems like ERP or HR platforms. This allows for automatic updates to roles when employees change positions or leave, reducing administrative work and ensuring your access controls remain up-to-date as you scale BI dashboards with AI automation [18].
Choose an access control system that scales effortlessly. Your solution should handle increasing numbers of users, roles, and permissions without performance issues. Look for systems that integrate smoothly with new technologies as your organization’s IT landscape expands [2].
Automate role assignments and use row-level security filters to manage real-time data access. Automation minimizes manual work and reduces the risk of human error, ensuring secure and efficient operations [18].
Define and document clear governance policies for creating, assigning, and managing roles. These policies should be well-documented and communicated across teams to ensure everyone understands their part in maintaining security standards. This level of governance helps build a resilient and long-term security framework for BI environments [1].
Leverage tools like Querio for advanced role management. Querio’s AI-driven role management system adapts to your business needs, offering a natural language interface and direct database connections. This allows teams, regardless of technical expertise, to securely access data while adhering to strict role-based controls. Its AI-powered custom dashboards and chart-building tools enable efficient, data-driven decision-making without compromising security.
The best BI security frameworks strike a balance between strong protection and user accessibility. By implementing these strategies and utilizing modern tools, organizations can safeguard sensitive information while empowering teams to maximize the value of their data assets.
FAQs
How can businesses implement role-based access control (RBAC) to align with their workflows and compliance needs?
To put role-based access control (RBAC) into action effectively, businesses should begin by defining roles that reflect the responsibilities tied to specific job functions. Permissions should then be assigned to these roles based on the tasks and data access needs required for each position. This approach ensures employees only access the information necessary for their work, helping meet compliance requirements like HIPAA or GDPR.
It's equally important to regularly review and audit roles and permissions. This keeps the system aligned with organizational changes and evolving compliance rules. Integrating RBAC into existing compliance frameworks can also make audits smoother and strengthen security by limiting sensitive data access to authorized individuals. By keeping RBAC well-organized and adaptable, companies can boost both security and operational efficiency.
How can organizations prevent permission creep and ensure their RBAC system stays secure over time?
To keep permission creep in check and uphold a secure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system, organizations can adopt a few essential strategies:
Stick to the principle of least privilege: Ensure users only have the access they absolutely need to perform their job duties - nothing more, nothing less.
Review access regularly: Take time to periodically evaluate user roles and permissions to align them with any shifts in responsibilities or organizational changes.
Audit permissions consistently: Conduct routine audits to spot and eliminate outdated or unnecessary permissions that could create security vulnerabilities.
These steps help organizations maintain a secure and efficient RBAC system that adapts to their ever-changing business landscape.
How do row-level and column-level security improve role-based access control (RBAC) in BI platforms?
Row-level security (RLS) and column-level security (CLS) add an extra layer of precision to role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring data access is tightly managed. RLS focuses on controlling access to specific rows within a dataset based on a user’s role. This means users only see the data that’s relevant to their responsibilities, minimizing the chances of unauthorized access and aligning with privacy regulations.
CLS takes a different approach by restricting access to particular columns. For example, sensitive details like financial data or personal identifiers can be hidden or masked, even for users who have access to the dataset as a whole. This ensures that individuals only view the information they’re permitted to see. When combined, RLS and CLS provide a secure and structured way to manage data access in BI platforms, promoting stronger compliance and more effective data governance.

