
Multi-Tenant Embedded Analytics Architecture
Business Intelligence
Dec 18, 2025
Practical guide to designing secure, scalable, and AI-driven embedded analytics that keep tenant data isolated in multi-tenant SaaS.

Multi-tenant embedded analytics allows SaaS applications to deliver analytics to multiple customers (tenants) on a shared infrastructure while keeping their data isolated. This approach integrates analytics directly into applications, enabling users to interact with data without leaving their workflow. It’s a cost-effective, scalable solution compared to traditional BI tools, which lack built-in multi-tenancy features.
Key Highlights:
Data Isolation Models: Options include shared databases with row-level security, separate schemas, or dedicated databases per tenant, each balancing cost, security, and complexity.
Benefits: Shared infrastructure reduces costs, speeds up feature rollouts, and supports self-service analytics for users.
Security & Compliance: Methods like encryption, row-level security, and identity management ensure tenant data remains private and meets U.S. compliance standards (e.g., HIPAA, SOC 2).
Performance & Scalability: Techniques like query optimization, caching, and tenant-specific resource allocation maintain speed as user bases grow.
AI Integration: Features like natural-language querying and personalized dashboards enhance user experience while maintaining strict data isolation.
Querio exemplifies this architecture by connecting directly to modern data layers, ensuring tenant isolation, and scaling efficiently with AI-driven insights and automated tenant management. It eliminates the need for complex ETL processes, making it a practical choice for SaaS providers embedding analytics.
Multi-Tenant Security for Embedded Analytics
Architecture Models for Multi-Tenant Analytics
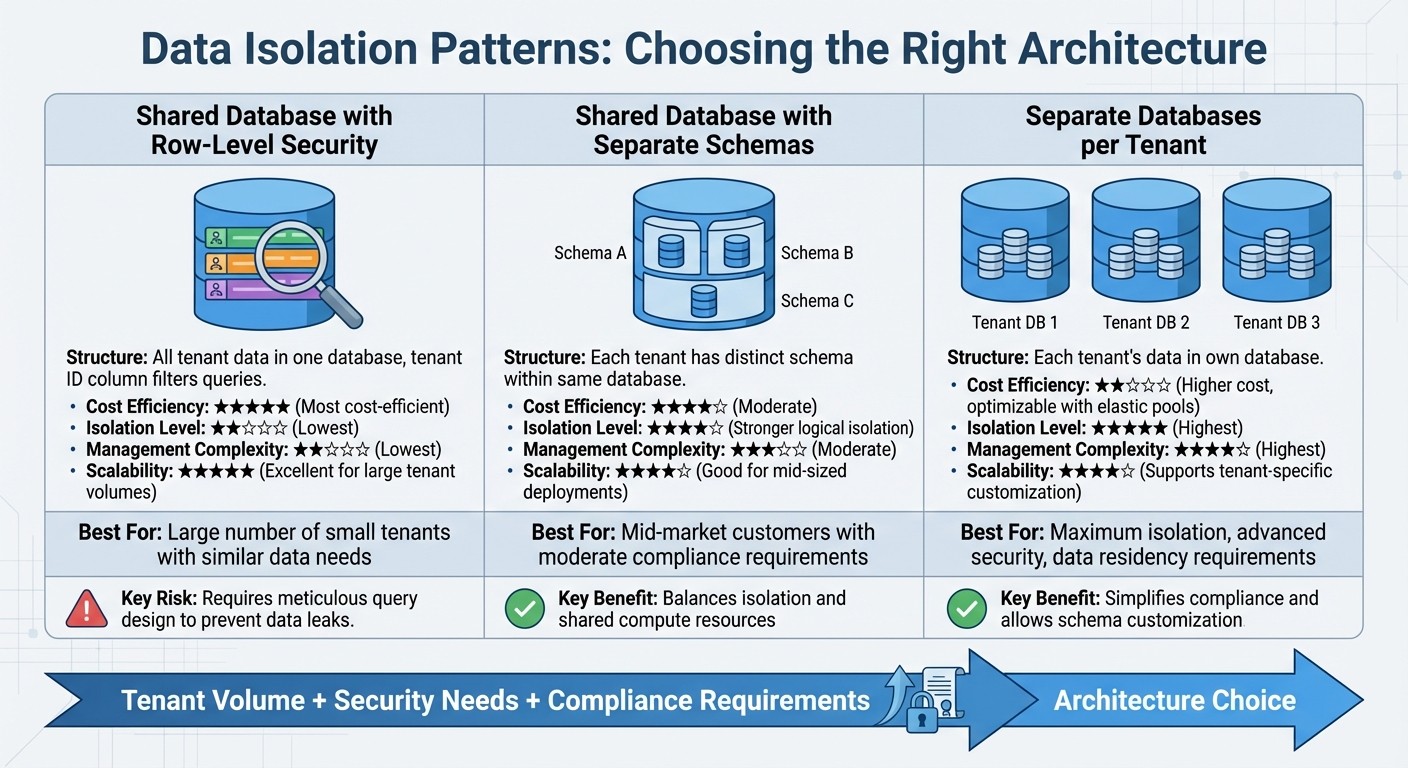
Multi-Tenant Data Isolation Architecture Models Comparison
These architecture models are key to delivering the performance and flexibility demanded by modern SaaS analytics platforms.
Tenants, Workspaces, and Embedded Experiences Defined
Before diving into the architecture patterns, let’s clarify a few essential terms. A tenant refers to a single customer organization using your SaaS application. This could be a company, a department, or any group requiring isolated access to their data. A workspace is a dedicated environment within your application where a tenant's users can collaborate, view dashboards, and generate reports - essentially enabling analytics tailored to their needs. The embedded experience refers to the analytics interface integrated directly into your application, allowing users to interact with data without leaving their workflow.
These elements form the foundation of a shared infrastructure. Each tenant is assigned a workspace equipped with analytics capabilities, and the challenge lies in keeping tenant data isolated while ensuring shared resources are managed efficiently to maintain performance.
With these terms clear, let’s explore the patterns that enable strong data isolation.
Data Isolation Patterns
Multi-tenant architectures typically fall into two categories: siloed models, where each tenant has its own storage construct, and pooled models, where tenant data is stored together but identified by a tenant-specific marker.
Here are three common patterns for data isolation:
Shared Database with Row-Level Security: In this approach, all tenant data resides in a single database, with a tenant identifier column used to filter queries. This model is cost-efficient and scales well to accommodate a large number of tenants. However, it requires meticulous query design to prevent data leaks as the data model evolves.
Shared Database with Separate Schemas: Each tenant is assigned a distinct schema within the same database. This offers stronger logical isolation compared to row-level security while still benefiting from shared compute resources. It’s a good fit for mid-sized deployments but involves higher management complexity.
Separate Databases per Tenant: Here, each tenant’s data is stored in its own database. This provides the highest level of isolation and security, allowing for tenant-specific schema customization. It also simplifies compliance with data residency requirements, especially for customers needing their data stored in specific regions. While this model can be costlier, elastic pools can help optimize costs by sharing resources across multiple databases.
Selecting the Right Architecture Model
The choice of architecture depends on factors like tenant volume, security needs, compliance requirements, and whether you build or buy your analytics platform. For scenarios with a large number of small tenants and similar data needs, a shared database with row-level security is a cost-effective option. For mid-market customers with moderate compliance requirements, separate schemas strike a balance between isolation and manageability.
When maximum isolation, advanced security, or tenant-specific schema customization is required, separate databases are the way to go. This model also supports data residency needs for customers requiring geographic-specific storage. While operational complexity may increase, automation tools for provisioning, backup, and monitoring can help streamline management.
Next, we’ll examine how these models influence security, governance, and compliance.
Data Security, Governance, and Compliance
When it comes to scalable multi-tenant analytics, security and compliance are non-negotiable. The architecture you choose directly impacts how you enforce security measures, control access, and meet regulatory demands.
Logical Data Isolation Methods
To ensure tenant data stays securely separated, logical security layers are essential. For example, Row-Level Security (RLS) allows queries to filter data based on user attributes, ensuring users only see records that belong to their tenant. Similarly, Column-Level Security can hide sensitive information, granting access strictly based on roles. In a shared database setup, RLS automatically filters queries so users only retrieve data relevant to their tenant.
Sensitive data can also be masked depending on user roles, offering an added layer of protection. Beyond data, asset permissions are crucial. These control access to dashboards, charts, and datasets, making sure users can’t view analytics content they’re not authorized to see - even if they somehow get a direct link. Additionally, system-level functions like publishing tools, embedding options, and user management should remain hidden from tenant users, reserved only for internal administrators.
Identity and Access Management
Authentication in a multi-tenant environment is best handled by established identity providers, rather than building a custom system. Single Sign-On (SSO) is a popular choice, letting users log in once and access analytics seamlessly without juggling multiple credentials.
In multi-tenant systems, it’s important to distinguish between internal platform users and tenant end-users. A unique client identifier (clientid) can help differentiate tenant users for features like personalization and download management. This separation avoids confusion between internal user accounts (used by employees creating content) and tenant user accounts.
For embedded analytics, JWT-based tokens are a secure way to pass user identity and permissions to embedded widgets. This approach maintains your existing security structure without duplicating user accounts across systems. Always encrypt sensitive configuration details when embedding analytics to keep your platform secure.
These authentication strategies are a solid foundation for embedded analytics security and meeting stringent US compliance standards.
US Compliance Requirements
By combining strong identity management and data isolation practices, your platform can meet regulatory frameworks like HIPAA and SOC 2. For industries handling sensitive information - such as healthcare or finance - compliance with standards like HIPAA, SOC 2, and GDPR (for EU data) is essential. These frameworks demand strict data separation, encryption for data at rest and in transit (using TLS and AES-256), and detailed audit trails to track who accessed data and when.
Audit logging is critical. Every action - data access, query execution, permission changes - should be recorded and forwarded to external monitoring systems like Splunk or Datadog for compliance purposes. For highly sensitive information, such as patient or financial data, field-level encryption provides an extra layer of security.
Querio’s architecture is built to support these requirements. With built-in encryption, customizable access controls, and activity logging, the platform ensures tenant data remains completely segregated. Its tenant workspace design guarantees that content created by one tenant is inaccessible to others, meeting even the strictest compliance standards. Moreover, resource tagging simplifies identifying tenant-specific infrastructure components, a key feature during audits or security checks.
"Put simply: you're not just embedding charts, you're embedding trust. Prioritizing data governance from day one makes scaling your analytics offering a whole lot easier." – Embeddable.com
Performance and Scalability Optimization
Delivering fast analytics to hundreds - or even thousands - of tenants takes more than just speeding up queries. The real challenge lies in maintaining that speed as your customer base grows, all while keeping infrastructure costs in check.
Performance Optimization Methods
Start by structuring your queries with a tenant_id filter. This not only speeds up execution but also ensures data remains isolated for each tenant. Pair this with proper indexing to further boost query performance.
Caching is another powerful tool. By storing frequently accessed results - like popular dashboard metrics or recurring report data - in memory, you can avoid redundant database queries. Precomputing aggregations during off-peak hours reduces latency, while routing heavy analytical queries to dedicated compute resources prevents one tenant's activity from slowing down others. This approach tackles the infamous "noisy neighbor" problem head-on.
These strategies lay the groundwork for a system that performs well even as it scales.
Scalability Strategies
Scaling horizontally is key. Add compute nodes or database replicas as needed, and allocate resources based on tenant usage. Stateless application layers and read replicas for analytics queries make this approach more effective, ensuring larger tenants get dedicated resources while smaller ones share resources efficiently.
To avoid resource contention during peak hours, stagger scheduled tasks like report generation and data refreshes. A well-managed job scheduler ensures no single tenant can monopolize compute capacity. If you're using a database-per-tenant model and managing thousands of tenants, disk overhead can become a challenge. Adjusting database engine settings - such as reducing partition counts or tweaking variables like log_file_size_partitions - can help manage storage costs. For shared database setups, using smaller, tenant-specific semantic models instead of one large model allows the system to prioritize active tenants and free up memory by evicting unused models. This setup balances resource use without sacrificing performance.
Querio's Performance and Scalability Features
Querio builds on these principles to deliver top-tier performance. By connecting directly to Snowflake, BigQuery, and Postgres in read-only mode, Querio eliminates data duplication and ETL delays. This ensures tenants always access the most up-to-date data.
Querio's AI-generated SQL takes optimization further by automatically applying tenant filters and leveraging the native performance features of your data warehouse. For advanced analysis, Querio's custom Python notebooks run on the same governed data, allowing data teams to create scalable, tenant-specific analytics. The semantic layer ensures consistent application of business logic and joins across all queries, removing the need for repetitive configurations or manual tuning for each tenant.
Embedding Analytics and Tenant Lifecycle Automation
Delivering a seamless user experience and maintaining efficient operations hinges on embedding analytics and automating tenant lifecycle processes. Once you've built a high-performing multi-tenant analytics system, the next step is to integrate insights smoothly and streamline tenant management to reduce operational headaches.
Embedding Patterns for Analytics
When it comes to embedding analytics into your application, there are three primary approaches to consider:
iFrame embedding: This is the simplest option. You embed your analytics within an iFrame and integrate it into your app. While it's quick to set up, it offers limited customization and may feel disconnected from your app's interface.
Component-level embedding: This method provides greater control by embedding individual charts, tables, or widgets directly into your app's UI using JavaScript SDKs. This approach creates a seamless experience, making analytics feel like an integral part of your application.
Full-page analytics portals: If you want to dedicate an entire section of your app to analytics, this is the way to go. It offers users a comprehensive workspace for exploring data and generating reports.
Choosing the right approach depends on how deeply you want analytics to integrate into your app. If analytics is a core feature for your users, component-level embedding or full-page portals often deliver a more cohesive experience than iFrames.
Beyond embedding, automating tenant lifecycle management is critical to ensure that scaling your tenant environments doesn’t come with added complexity.
Automating Tenant Lifecycle Management
Manually managing tenant provisioning and updates becomes unsustainable as your user base grows. Automation is essential. For example, when a new customer signs up, you can automatically create their workspace, configure data connections, apply security settings, and deploy dashboards. REST APIs can help you script this entire process, from onboarding to offboarding.
For ongoing updates, establish clear workflows for rolling out new reports or schema changes, whether to all tenants or specific groups. If you're using a database-per-tenant model, parameterize your semantic models so each tenant's analytics point to their own data source. For shared databases, tenant filters ensure users only see their data.
When a tenant leaves, automate the cleanup process. Delete their workspaces, revoke access, and archive data according to your retention policies. This not only prevents unused resources from piling up but also keeps your environment organized.
Tracking Usage and Costs per Tenant
Tracking usage and costs at the tenant level builds trust and helps optimize resource allocation. Monitor compute and storage consumption - track how many queries tenants run, how much data they process, and the warehouse time they use. This lets you calculate monthly costs in USD and identify which tenants are driving the highest infrastructure expenses.
Tools like Querio simplify this process by connecting directly to your data warehouse in read-only mode, avoiding the need for data duplication or costly ETL pipelines. Usage tracking happens at the warehouse level, with optimized SQL and automatic tenant filters ensuring efficient queries on shared resources. This approach keeps costs predictable while maintaining high performance for every tenant.
AI-Driven Personalization for Multi-Tenant Analytics
Building on strategies for performance and scalability, AI takes analytics to the next level by turning static dashboards into dynamic, conversational tools. The real challenge? Ensuring AI works seamlessly across hundreds - or even thousands - of tenants while keeping their data completely separate. Each tenant must receive tailored insights without any overlap or data leakage.
AI and Natural-Language Querying
Natural-language querying allows users to interact with data in plain English, skipping the need for complex SQL commands. For example, a user might type, "show me sales by region for Q4", and the AI translates this into a query, retrieves the data, and presents the results - all while maintaining strict tenant isolation. To achieve this, every query must include tenant-specific identifiers at each step.
When using stateful AI APIs, conversation histories should be stored using keys scoped to individual tenants, ensuring session data remains isolated. For advanced use cases like file searches or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), vector indexes must either be tenant-specific or enforce strict tenant filters on every query. Without these safeguards, a simple query like "show me customer data" could mistakenly pull records from the wrong tenant - a risk that must be avoided at all costs.
Personalization Strategies
AI doesn’t just answer queries; it can tailor the entire analytics experience to meet the needs of each tenant. Dashboards, metrics, and workflows can all be customized. For instance, a CFO might see KPIs relevant to financial health, while a product manager might focus on user engagement metrics. Even the way metrics are calculated can vary - for example, one tenant might define "active users" over a 30-day period, while another uses a 7-day window.
AI can also automate processes like anomaly detection, alerting tenants when their metrics deviate from historical trends. To refine the experience further, dedicated AI models can be deployed for individual tenants. These models allow for precise control over quotas, content filtering, and custom fine-tuning. While shared models help reduce operational complexity, they require careful tracking to allocate resources fairly and prevent any single tenant from overusing the system.
Querio's AI-Driven Personalization
Querio exemplifies how AI can transform multi-tenant analytics while prioritizing security and scalability. Its AI-native workspace connects directly to live data sources like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres, automatically applying tenant filters. Users can ask questions in plain English, and Querio’s AI leverages your semantic layer - complete with joins, metrics, and glossary definitions - to generate accurate charts in seconds.
For power users, Querio offers custom-built Python notebooks. These let users write SQL or Python for deeper analysis while still benefiting from AI assistance and governed data access. Because Querio operates in a read-only mode, tenant isolation is maintained even when AI executes queries. This setup also keeps costs transparent, with no hidden query fees, and ensures personalization scales effectively without compromising security or performance.
Conclusion
Creating a multi-tenant analytics architecture is all about balancing scalability, security, and personalization. The ideal setup should scale smoothly with user growth without skyrocketing costs, ensure strict tenant isolation at every level, and provide tailored experiences that cater to diverse customer needs. Ignoring any of these priorities risks compromising security, driving up expenses, and alienating users.
Traditional BI tools often fall short in supporting multi-tenancy out of the box, requiring expensive customizations to fill the gap. This challenge has opened the door for platforms specifically designed for multi-tenant environments.
Take Querio, for example. It sets the standard for modern multi-tenant analytics platforms. With its AI-native workspace, Querio connects directly to live data sources like Snowflake, BigQuery, and Postgres, automatically applying tenant filters. This means users from different tenants can simply ask questions in plain English and receive accurate, tailored insights instantly - all while data teams maintain control through a consistent semantic layer. Plus, with features like read-only access, no hidden query fees, and SOC 2 Type II compliance, Querio ensures top-tier security, performance, and customization.
Its architecture also supports both shared and separated dataset models, offering flexibility to meet specific security or compliance needs. Whether you aim to maximize resource efficiency or physically separate tenant data for added security, Querio adapts to your requirements. Features like automated content deployment and tenant lifecycle management make it easier to handle operations, even at scale with thousands of tenants. This adaptability allows SaaS companies to make smarter, more strategic decisions.
For SaaS providers embedding analytics, the choice boils down to building a solution from scratch or leveraging one of the best multi-tenant analytics platforms. Querio’s model - blending AI-driven personalization, strong security measures, and proven scalability - illustrates how embedded analytics can thrive in today’s multi-tenant environments.
FAQs
How does a multi-tenant architecture ensure data is secure and isolated?
Multi-tenant architectures prioritize data security and isolation by using a mix of physical and logical separation methods. Tenant data can be stored in several ways - dedicated schemas, separate databases, or even isolated infrastructure like individual compute clusters. In cases where shared tables are used, techniques like row-level security and tenant-specific identifiers ensure that users can only access their own data.
To tighten security further, role-based access control (RBAC) assigns permissions tailored to tenant-specific roles, while token-based authentication ensures only authorized users gain access. Data is encrypted both at rest and during transit, and strict network policies block unauthorized access. On top of that, audit logs capture all activities, enabling quick detection of any suspicious behavior. Together, these measures create a secure and dependable environment for multi-tenant systems.
What are the main advantages of integrating analytics directly into SaaS applications?
Integrating analytics into SaaS applications brings a range of advantages that can significantly enhance both functionality and user experience.
One major benefit is the reduction in infrastructure and operational costs. By using a shared analytics engine to serve multiple customers, while ensuring their data remains securely separated, SaaS providers can streamline maintenance and updates. This means any changes or improvements are applied once to the core system, cutting down on time and effort.
Another key advantage is the ease of scalability. Multi-tenant architectures allow resources to be allocated dynamically, making it simple to onboard new users quickly without driving up costs. This setup ensures a smooth user experience, complete with real-time dashboards and AI-powered insights that support better decision-making and boost user engagement.
Lastly, personalization and branding become much more accessible with embedded analytics. SaaS providers can tailor visualizations, access controls, and workflows to align with each client’s unique needs. This level of customization not only enhances adoption but also strengthens client retention by delivering a tailored experience.
These benefits highlight why embedded analytics has become a must-have feature for modern SaaS platforms.
How does AI-driven personalization improve the user experience in multi-tenant analytics platforms?
AI-powered personalization takes multi-tenant analytics to the next level by automatically adjusting insights, visualizations, and recommendations to fit each tenant’s specific needs and objectives. By evaluating user behavior and the broader business context, AI can surface the most relevant KPIs, propose tailored dashboards, and even generate narrative summaries using language that resonates with the tenant’s industry - all without requiring manual intervention.
These advanced AI features are seamlessly integrated into the analytics interface, offering real-time, context-aware support. For instance, when a user explores a chart, the AI might recommend related metrics, highlight unusual trends, or provide concise summaries based on the tenant’s historical data. This personalized approach not only helps users uncover actionable insights faster but also simplifies the platform for newcomers and delivers a scalable, user-friendly experience for all tenants.

