
Stitching LLMs and data together with the power of semantic layers
Business Intelligence
Dec 11, 2025
Semantic layers give LLMs business context—standardizing metrics, joins, and access controls so models deliver accurate, governed BI.

Semantic layers simplify how large language models (LLMs) interact with raw enterprise data. They standardize messy databases, align business logic, and improve query accuracy. Without them, LLMs often misinterpret data, leading to errors and unreliable outputs. By acting as a bridge, semantic layers organize data into clear metrics, relationships, and definitions, enabling LLMs to generate precise insights.
Key Points:
What is a semantic layer? A system that translates raw data into accessible business terms, like turning "rev_amt_usd" into "revenue."
Why do LLMs need it? LLMs lack business context and struggle with raw data. Semantic layers improve their accuracy in generating SQL queries or insights.
Benefits: Improved accuracy (e.g., GPT-4's SQL query accuracy increased from 16.7% to 54.2%), faster insights, and reduced human intervention.
How it works: A semantic layer defines metrics, joins data tables, and ensures consistent results, acting as a single source of truth for organizations.
Querio exemplifies this approach by integrating semantic layers with LLMs to deliver accurate, governed, and secure insights from raw data warehouses like Snowflake or BigQuery. With Querio, users can ask natural language questions and receive precise answers, eliminating the need for technical expertise.
Semantic Layer + LLM = AI Chatbot for Fast Answers
Foundations of Semantic Layers and LLMs
To understand how semantic layers and large language models (LLMs) complement each other, it’s important to first break down what each does well - and where they fall short individually.
Key Components of Semantic Layers
A semantic layer serves as a bridge between raw data and its users by transforming complex datasets into standardized, actionable insights. It does this through several core elements:
Metadata: This defines the meaning and structure of each data point, ensuring clarity.
Business glossaries: These establish consistent terminology across an organization, so everyone is aligned when discussing metrics like "revenue" or "customer lifetime value."
Taxonomies and ontologies: These organize and map relationships between various data concepts.
Knowledge graphs: These visually represent how data points connect, making relationships easier to understand.
Together, these components create a unified and governed interface that simplifies the complexity of data warehouses, lakes, and lakehouses. The result is a single source of truth for metrics and definitions. Without this structure, LLMs struggle to interpret raw data effectively.
Challenges of LLMs with Raw Data
When LLMs attempt to work directly with raw enterprise data, they encounter significant obstacles. The primary challenge is the absence of business context. Raw data is often fragmented, cryptically labeled, and devoid of clear meaning. For example, an LLM cannot inherently determine if "amt" refers to dollars, units sold, or customer count. It also lacks the ability to understand how datasets should be joined or the intricacies of their relationships. This lack of clarity can lead to errors like hallucinations or inconsistent outputs, making the results unreliable. These limitations highlight why LLMs alone are insufficient for generating meaningful business intelligence.
How Semantic Layers Address LLM Challenges
Semantic layers solve these issues by providing structured logic and consistent definitions. Instead of leaving LLMs to guess how to interpret data, the semantic layer supplies predefined rules and relationships. This includes:
Standardized definitions for metrics and terms
Proper join logic for combining datasets
Clear business rules to guide data interpretation
Architecture Patterns for LLMs, Semantic Layers, and Data Warehouses
Creating a powerful AI-driven analytics system means understanding how its different layers work together. Typically, this architecture includes four key components: a data warehouse (like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres), a semantic layer that defines business logic and relationships, an LLM interface that processes natural language queries, and a governance layer that manages security and access controls. Each element serves a distinct purpose in transforming plain English questions into secure, accurate insights. This layered setup ensures a smooth and reliable process for query translation.
Core Components of the Architecture
At the base of the system is the data warehouse, which stores the raw data for the organization. Sitting above it is the semantic layer, which holds business definitions, metric calculations, and rules for how tables should connect. The LLM interface takes user queries, relying on the semantic layer to provide the context needed for accurate data retrieval. Finally, the governance layer ensures the system adheres to security protocols, including role-based access, data masking, and compliance policies. Together, these layers ensure that even when an LLM generates a query, it only accesses data the user is permitted to see.
Integration Workflow Examples
Let’s break down how this integration works in practice. Suppose someone asks, "What were our Q3 sales by region?" The LLM begins by interpreting the intent behind the query, identifying "Q3" as the time period, "sales" as the metric, and "region" as the dimension. The semantic layer steps in to provide exact definitions for where the data lives, how metrics are calculated, and how tables should join. Using this information, the LLM generates a precise SQL query to run against the data warehouse. The results are then presented as a chart or table. By relying on the semantic layer, the system minimizes errors in joins and reduces the likelihood of generating inaccurate results.
How Querio Implements the Architecture
Querio takes this layered approach and integrates each component seamlessly. It connects directly to data warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres using secure, read-only credentials. Its semantic layer allows data teams to define business logic by setting up table relationships, metric formulas, and a glossary of terms. When users ask questions in plain English, Querio’s LLM uses this framework to generate SQL queries and deliver accurate visualizations. For more advanced tasks, Querio’s AI Python notebooks let analysts write code against the same governed data, ensuring consistency across simple queries and complex models. The system is also built to maintain SOC 2 Type II compliance and ensure 99.9% uptime, providing reliability and security at every step.
Designing a Semantic Layer for LLM-Driven Analytics
A well-designed semantic layer provides LLMs with the business context they need, without overloading them with technical details. The aim is to build a structured framework that removes ambiguity and ensures consistent, accurate responses to queries - whether they're coming from a CEO or a data analyst. This layer acts as the single source of truth for your organization.
Best Practices for Modeling Semantic Layers
To ensure your semantic layer delivers reliable and actionable results, follow these key practices:
Define canonical metrics: Establish agreed-upon formulas for metrics like revenue, churn rate, and customer lifetime value. These should be stored in one central location to maintain consistency across the organization.
Standardize business vocabulary: Create a glossary that links everyday terms to their technical equivalents. For example, if your sales team refers to "active customers" but your database uses "users_with_purchase_last_90_days", the semantic layer should bridge this gap seamlessly.
Clarify table joins: Explicitly define how tables connect to avoid confusion when queries are run.
Incorporate time intelligence: Predefine fiscal quarters, rolling windows, and year-over-year comparisons so the system handles date calculations accurately.
Centralize complex logic: Use reusable calculations or macros for intricate formulas. For instance, if your margin calculation involves multiple cost categories, define it once in the semantic layer instead of repeating it in every query.
Support synonyms and tags: Help the LLM interpret user intent by mapping terms like "income", "earnings", and "profit" to the same metric.
Governance and Security Considerations
Strong governance and security are essential for a reliable semantic layer. According to an MIT survey, 59% of respondents cited data governance, security, or privacy as their top concern when linking private data to LLMs. The semantic layer is where these protections come into play.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Integrate RBAC into your semantic definitions to automatically filter data based on the user's permissions. For example, a regional manager should only see data for their territory, even if their query is broad.
Metadata accuracy: Precise metadata reduces errors. Google’s internal tests revealed that Looker’s semantic layer cut data mistakes in generative AI queries by up to two-thirds. While LLMs can hallucinate incorrect responses 15-20% of the time, grounding them with accurate business definitions significantly improves reliability.
Security measures: Use encryption for data in transit and at rest, multifactor authentication, and enforce compliance with standards like SOC 2, HIPAA, and ISO. The semantic layer should also include built-in data quality checks and maintain audit trails to track data access and usage.
These steps not only protect sensitive information but also ensure that AI-generated insights remain trustworthy, reinforcing the semantic layer as the backbone of your organization’s analytics.
Querio's Approach to Semantic Layer Design
Querio simplifies semantic layer management by centralizing all business context - table joins, metric definitions, and term glossaries - in one place. This allows data teams to define metrics and rules once, ensuring consistent governance over time. When someone asks a question in plain English, Querio’s LLM uses this semantic layer to generate precise SQL. The same definitions power dashboards, AI Python notebooks, and other tools, ensuring uniformity across various use cases.
Querio’s platform connects securely to major data warehouses with read-only access, maintaining SOC 2 Type II compliance and 99.9% uptime. By treating the semantic layer as an evolving system, Querio ensures that any updates to metrics or definitions are automatically reflected in all downstream analyses. This approach integrates seamlessly with Querio’s broader AI-driven analytics framework, delivering secure and accurate insights every time.
Implementing LLM-Powered BI Using Querio
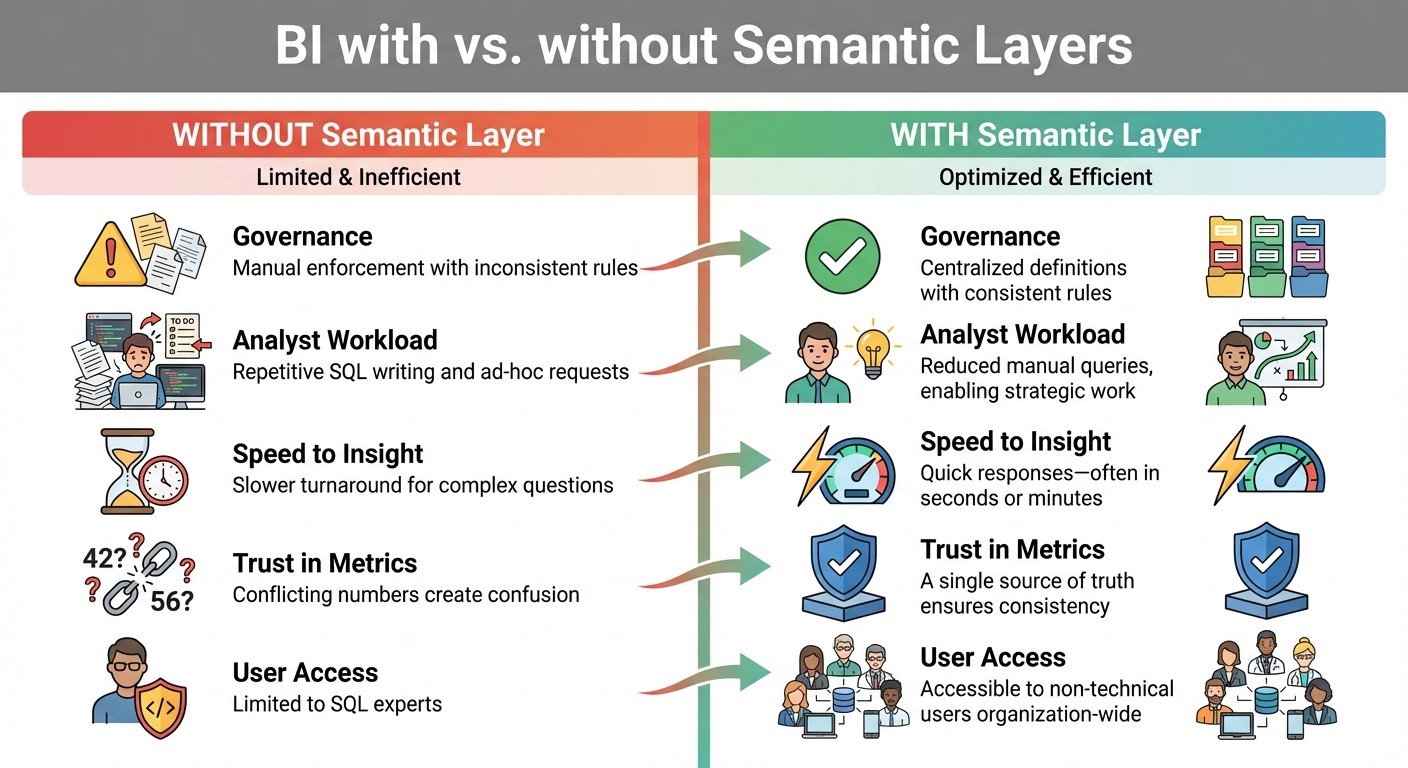
BI Workflows: With vs Without Semantic Layers
Creating a seamless journey from raw data to actionable insights is key to leveraging LLM-powered BI effectively. At the heart of this process is the semantic layer, which bridges business questions and accurate data queries while ensuring governance and security. Querio simplifies this by connecting directly to your data warehouse and adding a layer of business context, enabling anyone to ask questions in plain English - no SQL or Python required.
End-to-End Workflow with Querio
To get started, connect Querio to your data warehouse - whether it’s Snowflake, BigQuery, or Postgres - using read-only, encrypted credentials. Next, build a semantic layer that reflects your business logic. For instance, if your finance team needs to understand "monthly recurring revenue", the semantic layer identifies the necessary tables and calculations to provide that insight.
Once the semantic layer is in place, users across your organization can ask questions like, "What was our churn rate in Q3?" or "Show me revenue by region for the last six months." Querio’s large language model interprets these queries, writes the corresponding SQL, and delivers results as charts or tables in seconds. This same layer also powers drag-and-drop dashboards for monitoring KPIs, scheduled reports to keep leadership informed, and embedded analytics that bring insights directly to your end users. For deeper analysis, Querio’s AI Python notebook allows for advanced queries on governed data.
Considerations for Scalability and Reliability
Defining the workflow is just the beginning; ensuring scalability and reliability is equally important. As your organization grows, your BI platform must keep pace without compromising performance. Querio supports this with 99.9% uptime and SOC 2 Type II compliance, offering enterprise-grade reliability and security. Its read-only connection model safeguards against unintended data changes, while encryption ensures credentials and data remain secure during transit.
Monitoring LLM outputs is essential to catch misinterpretations or edge cases. Thanks to the centralized semantic layer, updates to metric definitions or table joins are automatically reflected across dashboards, notebooks, and natural language queries - eliminating the need for manual adjustments across various tools. Additionally, Querio’s architecture supports unlimited viewer users, making it easy to scale access as more people in your organization need insights.
Comparing BI with and Without Semantic Layers
The advantages of a semantic layer become clear when you contrast traditional BI workflows with those powered by LLMs. Without a semantic layer, analysts often spend hours translating business questions into SQL, managing conflicting metric definitions, and manually enforcing data access rules. With a semantic layer, these processes are streamlined and standardized, saving time and reducing complexity.
Aspect | Without Semantic Layer | With Semantic Layer |
|---|---|---|
Governance | Manual enforcement with inconsistent rules | Centralized definitions with consistent rules |
Analyst Workload | Repetitive SQL writing and ad-hoc requests | Reduced manual queries, enabling strategic work |
Speed to Insight | Slower turnaround for complex questions | Quick responses - often in seconds or minutes |
Trust in Metrics | Conflicting numbers create confusion | A single source of truth ensures consistency |
User Access | Limited to SQL experts | Accessible to non-technical users organization-wide |
Conclusion
Semantic layers serve as the crucial bridge that elevates large language models (LLMs) from being just powerful language processors to becoming dependable tools for business intelligence. Without this structured framework, even the most advanced models can misinterpret raw data, deliver inconsistent metrics, or create connections that don’t actually exist.
By combining semantic layers with LLMs, businesses can completely transform how data is accessed and how quickly insights are delivered. Instead of waiting days for analysts to translate business questions into SQL queries, teams across an organization can simply ask questions in plain English and receive accurate, governed responses within seconds. This approach not only makes data more accessible but also ensures it remains secure and reliable - a game-changer for modern analytics.
Querio exemplifies this integration by directly connecting to your data warehouse, applying business context once, and allowing anyone to query governed data using natural language, drag-and-drop dashboards, or AI-powered Python notebooks. With a focus on compliance and reliability, Querio delivers insights that are secure and accurate without the complexity of traditional business intelligence tools.
The benefits are clear: consistent and accurate insights where metric definitions remain aligned, access rules are automatically enforced, and your data team can shift their focus to high-value strategic work instead of handling repetitive ad-hoc requests. Whether you’re a finance leader monitoring monthly recurring revenue or a product manager studying user behavior, the semantic layer ensures you’re working with actionable, contextual insights - not raw data that requires expert interpretation.
As LLMs continue to advance, the key to unlocking their full potential lies in building a strong semantic layer. This foundation captures your business logic, governs your data, and empowers everyone in your organization to harness the power of AI-driven analytics effectively and securely.
FAQs
How do semantic layers enhance the accuracy of insights from large language models (LLMs)?
Semantic layers play a crucial role in improving the precision of insights produced by large language models (LLMs). They provide a structured framework that helps LLMs interpret data within the correct business context, understand relationships, and use accurate terminology. This reduces errors and lowers the chances of generating misleading or inaccurate responses.
By serving as a connection point between complex datasets and natural language queries, semantic layers enable LLMs to deliver results that are not only more accurate but also consistent and easier to understand. This structured approach strengthens data governance, aligns insights with organizational metrics and definitions, and supports quicker, more dependable decision-making.
What are the key components of a semantic layer and how do they work?
A semantic layer relies on several essential components: metadata, taxonomy and information architecture, business glossary, ontology, and knowledge graph. Together, these elements create a structured and standardized framework for organizing data, making it more accessible and easier to analyze.
Metadata describes the data in detail, covering aspects like its source, structure, and purpose. Think of it as the "who, what, and why" of your data.
Taxonomy and information architecture focus on categorizing and organizing information consistently, ensuring everything is easy to locate and understand.
A business glossary defines terms and concepts in a standardized way, helping teams communicate clearly and avoid misunderstandings.
Ontology maps out formal relationships between data elements, while the knowledge graph links these elements together to provide context and deeper insights.
When these components work in harmony, they make natural language queries more intuitive and enhance data accessibility. They also strengthen governance and streamline decision-making processes.
How does Querio protect data and ensure compliance with industry standards?
Querio places a strong focus on keeping data secure and compliant. It achieves this through the use of encryption technologies, role-based access controls, and strict data management policies. These safeguards ensure that sensitive information stays protected and that only the right people can access specific datasets.
On top of that, Querio aligns with recognized industry standards and regulations, ensuring data privacy and integrity are upheld throughout its system. This gives businesses the confidence to manage their data securely while staying within compliance guidelines.

