The Evolution of Business Intelligence with AI
Business Intelligence
Feb 1, 2026
AI is reshaping business intelligence with natural-language queries, automated and predictive insights, governed semantic layers, and real-time analytics.

Business Intelligence (BI) has shifted from static reports to AI-powered tools that deliver instant, actionable insights. AI now enables users to ask plain-English questions, automates data analysis, and predicts future trends, making data accessible to everyone - not just analysts. Companies like Walmart and Swiggy have already seen massive gains, such as a 173% increase in customer engagement and real-time anomaly detection.
Key Takeaways:
AI Features in BI: Natural language querying, automated insights, predictive analytics, and explainable AI.
Efficiency Gains: AI reduces manual tasks like data cleaning and improves decision-making speed.
Real-World Impact: Examples include Walmart's shopper insights platform and Northmill's 30% boost in conversion rates.
Governance: Semantic layers ensure consistent data definitions and compliance.
Future Trends: Real-time analytics and agentic AI are transforming decision-making.
AI-driven BI tools are changing how businesses operate by providing faster, more accurate, and predictive insights while empowering non-technical users to access data effortlessly.
From Traditional BI to AI-Driven Intelligence
What Traditional BI Gets Wrong
Traditional business intelligence (BI) systems, designed for an earlier era, often tie up analysts with manual tasks - up to 92% of their time - leaving little room for strategic thinking. This inefficiency is baked into their design.
The main flaw lies in their retrospective nature. These tools excel at answering "what happened" by analyzing historical data but fall short when it comes to predicting "what will happen" or advising "what should we do next." By the time insights are generated, markets or conditions may have already shifted, rendering the data less useful.
Another issue is accessibility. Traditional BI systems often require SQL expertise, which means 75% of employees lack direct access to these tools [3]. Those without SQL skills are left dependent on IT teams or forced to rely on intuition. The static dashboards provided by these systems further exacerbate the problem, offering generic, one-size-fits-all views that fail to address specific team needs or adapt to follow-up questions.
These shortcomings highlight why AI has become a critical evolution in the BI landscape.
How AI Improves Business Intelligence
AI takes BI to the next level by delivering instant, actionable insights and eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional systems. Instead of requiring technical expertise, users can ask plain-English questions like, "What were the regional sales trends over the past six months?" and receive immediate, visualized answers. This is made possible by Natural Language Querying (NLQ), which removes the SQL barrier and turns BI into a more intuitive, conversational experience.
AI doesn't just describe past data - it shifts BI into predictive and prescriptive analytics, offering forecasts and actionable recommendations. For example, in 2024, the neobank Northmill used AI-driven analytics to optimize its customer onboarding process. By pinpointing where users were dropping off, they adjusted their workflow and saw a 30% boost in conversion rates.
Routine tasks like data cleaning, schema mapping, and quality checks are also automated with AI, freeing analysts to focus on higher-value work. Take Wellthy, a caregiving company, as an example. By leveraging natural language search, their care team could access real-time patient data without needing help from the data team. This self-service approach saved the company over $200,000 by significantly improving efficiency.
"Traditional BI systems, primarily reliant on historical data analysis and manual interpretation, are increasingly supplanted by AI-augmented frameworks." - Visweswara Rao Mopur, Principal Architect, Invesco Ltd [4]
AI also excels at real-time anomaly detection. It can scan massive datasets in seconds to identify patterns that would otherwise go unnoticed - like fraud attempts, supply chain disruptions, or sudden changes in customer behavior. Instead of waiting weeks for these issues to surface in a report, businesses can act immediately while solutions are still viable. This ability to deliver insights when they matter most underscores the transformative impact of AI on decision-making.
Business intelligence in the age of AI - what's the future of BI??
Core AI Features in Modern BI Platforms
Modern BI platforms have evolved far beyond static dashboards, integrating AI to provide actionable and predictive insights. This shift has redefined how businesses interact with data, making analytics more accessible, automating insights, forecasting outcomes, and ensuring transparency. Here's a closer look at the key features driving this transformation. These essential features of modern BI tools empower teams to make data-driven decisions faster.
Natural Language Querying (NLQ)
Natural Language Querying (NLQ) breaks down technical barriers by enabling users to interact with data using plain English. For instance, a marketing manager could type, "What were our top-performing products in the Northeast last quarter?" and instantly receive a visualized response [6][7].
Today, NLQ systems boast impressive accuracy - Snowflake's Cortex Analyst, for example, achieves around 90% accuracy when converting natural language into SQL for structured data [7]. Companies like Virgin Atlantic have embraced this technology through tools like Databricks AI/BI Genie, cutting their booking analysis time from weeks to mere hours in 2024 [5]. Similarly, SEGA Europe reported a tenfold improvement in time-to-insight by enabling managers and engineers to retrieve answers instantly [5].
The results speak volumes. Wineshipping found that 75% of its target users actively engaged with data weekly after implementing AI-driven self-service dashboards [5].
Automated Insight Generation
AI takes the initiative by scanning data to highlight trends, anomalies, and correlations, eliminating the need for users to identify patterns manually. For example, it can flag critical events like a rise in customer churn, inventory shortages, or unexpected revenue changes.
Italgas reported a 73% reduction in workload costs after implementing AI-driven insights, freeing analysts to focus on strategic tasks rather than routine monitoring [5]. These systems also create automated narratives to explain changes, their significance, and potential next steps.
"AI is making data less about numbers and more about insightful stories that every team member can read and understand." - Improvado [5]
One retailer in the Middle East used AI forecasting within Microsoft Power BI to improve stock accuracy by 20% and reduce out-of-stock incidents by 30%, thanks to its ability to predict demand patterns before they became problematic [10].
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
Predictive analytics shifts BI from analyzing past events to forecasting future outcomes. Machine learning models analyze historical data, seasonal trends, and external factors to generate predictions that inform better planning and strategy. This approach allows businesses to be proactive rather than reactive.
For instance, GlobalMart, a multinational retailer, used AI-driven demand forecasting to optimize inventory, resulting in an 18% reduction in inventory costs and a 22% increase in sales through personalization [11]. Similarly, FutureBanc, a European digital-first bank, adopted predictive risk assessments, leading to a 40% drop in customer service costs and a 25% decrease in loan defaults [11].
The integration of multiple AI technologies - such as natural language processing for sentiment analysis and machine learning for behavioral predictions - further enhances these platforms' ability to address complex business challenges [7][8].
Explainable AI (XAI)
Explainable AI (XAI) ensures transparency by showing how data is analyzed and interpreted. Unlike "black-box" systems, XAI provides clear visibility into the steps taken to generate insights, from the data sources used to the filters applied and the logic behind conclusions. This level of transparency is crucial for regulatory compliance and building user trust.
Modern BI platforms often display generated SQL or Python code for verification and include data lineage visualizations to trace insights back to their source [7][12].
"Most AI products fail not because the model is wrong, but because users don't understand what it's doing." - Natalia Yanchiy, Eleken
A great example is Wells Fargo's AI-driven fraud detection system, which analyzes millions of transactions in real time. It flags suspicious activities for human review, providing clear explanations for each flagged transaction. This approach has saved millions of dollars by intercepting fraud while maintaining accountability [6].
XAI also ensures predictive models are auditable. For example, when forecasting a sales decline in a specific region, the system breaks down contributing factors like trends and seasonality, helping users understand the rationale behind the prediction [9].
Summary of Key Features
Feature | How It Works | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
Natural Language Querying | Translates plain English into SQL/Python queries | Expands data access; 75% of users engage with data weekly [5] |
Automated Insights | Flags trends, anomalies, and correlations automatically | Cuts analyst workloads by 73%; uncovers hidden opportunities [5] |
Predictive Analytics | Uses machine learning to forecast outcomes | Reduces costs by 18%-40%; boosts performance by 22%-30% [10][11] |
Explainable AI | Shows reasoning, code, and data lineage | Builds trust, supports compliance, and enables human oversight [12] |
Self-Service Analytics with Governance
AI gives employees the ability to dive into data and draw their own insights. But with this freedom comes a challenge: how do you ensure everyone sticks to the same definition of key metrics, like "revenue"?
The answer lies in governed semantic layers - a centralized system that standardizes business definitions and streamlines data exploration. Without governance, teams might calculate the same metric differently, leading to conflicting reports and eroding trust in the data. A unified approach ensures consistency and reliability, creating a solid foundation for self-service analytics.
Governed Semantic Layers
Think of a semantic layer as the backbone of your organization's data consistency. It acts as a single source of truth, ensuring that every query uses the same definitions for key metrics and terms.
This layer translates complex database structures into everyday business language. For example, when someone asks, "What was our revenue last quarter?" the AI pulls from model metadata - like table relationships, column descriptions, and synonyms - to provide the correct answer in the right business context.
Data teams can go a step further by developing AI Data Schemas to prioritize relevant data and remove unnecessary clutter. For more complex queries, they can define Verified Answers or Trusted Assets - pre-approved query patterns the AI relies on when specific trigger questions arise.
The benefits are clear. Gartner estimates that by 2026, 60% of AI projects will fail without AI-ready data [14]. On the flip side, companies using natural language interfaces built on semantic layers report a 70% efficiency boost in handling routine data queries [5].
"A semantic layer can help you create consistent, reusable assets to serve as a single source of truth and unlock the full potential of your data by enriching it with business knowledge."
Daniel Alon, Senior Vice President, Product Management, Salesforce [14]
Modern platforms take this further by integrating semantic layers with governance tools like Unity Catalog. These tools offer features like lineage visualization and compliance with global security policies, all without requiring data extraction.
Empowering Non-Technical Users
Governed semantic layers don’t just ensure consistency - they also make data accessible to everyone, regardless of technical expertise. Natural language interfaces remove the need for SQL skills or navigating complex systems, while governance ensures compliance and accuracy.
Take SEGA Europe, for example. They achieved a 10x faster SQL creation rate using natural language queries, allowing executives and marketers to get instant answers without manual coding [5].
The trick is balancing accessibility with control. Data teams can limit visibility by hiding technical or sensitive fields from the AI, preventing unauthorized outputs. They can also roll out AI features gradually, targeting specific security groups after proper training.
To make these systems even more effective, teams should focus on enriching metadata. This includes adding clear field descriptions, adopting intuitive naming conventions, and using synonyms. For instance, renaming a column like "TR_AMT" to "Total Revenue" helps the AI interpret queries correctly. Features like "Prep for AI" can also guide the AI with unstructured instructions, such as defining "Peak Season" as November through January or specifying fiscal quarters as the default analysis period.
The results speak for themselves. Companies using natural language analytics self-service dashboards report that 75% of target users engage with data weekly [5]. This level of adoption is only possible when users trust their insights to be accurate, consistent, and compliant - something governed semantic layers are designed to deliver.
How to Implement AI-Driven BI
Transitioning from traditional BI to AI-powered analytics requires careful planning, thoughtful integration of AI tools, and systems that ensure reliable results. Most organizations can enhance their existing data infrastructure with AI capabilities by following key steps.
Data Preparation: The Foundation
Before deploying any AI tool, start with thorough data preparation. Evaluate your data's maturity by reviewing schema complexity, metadata coverage, naming consistency, and table relationships [15]. If your data environment is chaotic - lacking metadata, using inconsistent naming, or having unclear relationships - AI query accuracy will suffer. Conversely, well-organized data with consistent naming and comprehensive metadata significantly boosts accuracy.
"According to BCG's research on AI transformation, algorithms account for only 10% of the work, the tech backbone for 20%, and the remaining 70% depends on people and processes." [18]
This highlights why preparing your data is more critical than focusing solely on the AI model itself. A strong data foundation paves the way for seamless AI integration into BI workflows.
Building a Semantic Context Layer
A semantic context layer bridges the gap between business language and database structure. For instance, if someone asks, "What was our churn rate last quarter?" the AI uses this layer to interpret terms, join tables, and calculate metrics according to your organization’s standards.
Without a well-defined semantic layer, AI tools may make incorrect assumptions, resulting in flawed joins, inconsistent metrics, and lost trust. To address this, ensure your semantic layer enforces consistent business definitions. Many teams now use lightweight YAML files to define semantic models [16][13]. Start by creating a business term registry that maps everyday language to technical definitions. For example, "active users" might mean different things to your product and finance teams. Document these variations, establish standard definitions, and encode them into your semantic layer [15]. Modern tools integrate semantic layers with governance frameworks like Unity Catalog, offering traceability from raw data to final insights [19][8].
Integrating AI Agents
Once your semantic layer is ready, you can introduce AI agents that convert natural language into executable SQL or Python. These agents analyze queries, plan strategies, and execute workflows [18].
The integration approach matters. Many organizations use a "Manager" orchestration model, where a central coordinator delegates tasks to specialized sub-agents [17][20]. For example, a complex user query might trigger an SQL generation task for a BigQuery agent, while a Python-based agent handles visualizations. This structured delegation keeps the system organized and manageable.
Virgin Atlantic provides a clear example. By integrating natural language query capabilities with Unity Catalog, the airline cut booking analysis times from weeks to just hours [5].
Start with a shadow mode setup, where the AI suggests queries and visualizations but requires human approval before execution [18]. This allows you to validate the agent’s logic without risking operations. As confidence builds, move to "Guided Autonomy", where the agent operates within predefined limits, leaving exceptions for human oversight.
Clearly define tool boundaries for your AI agents. Assign them specific data access, actions, and orchestration tools, all governed by role-based access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data through natural language queries [15][16].
Ensuring Data Integrity and Explainability
For AI-driven BI to succeed, users need to trust the insights it generates. Every AI-produced result should include a transparent explanation of the logic behind it. For instance, when a system translates "Show me revenue by region" into SQL, users should be able to review the generated SQL query [16][15]. This transparency fosters trust and provides a feedback loop to improve the semantic layer.
Set up guardrails and real-time query validation to catch issues like missing filters or inefficient joins. Combine large language model (LLM)-based classifiers with rules-based protections, such as regex patterns to prevent SQL injection [15][17].
Italgas, a gas distribution company, unified its data architecture with AI-driven BI and reduced workload costs by 73% through real-time, governed insights [5].
Incorporate human-in-the-loop feedback systems to capture user corrections and implicit signals, like query rephrasing [19][15]. This ongoing feedback refines semantic definitions over time, improving accuracy without constant manual updates.
Lastly, maintain detailed audit trails. Record every prompt, generated query, and user action - whether approval or rejection. This not only supports compliance but also aids debugging when results are unexpected. Snowflake's Cortex Analyst demonstrates how, with proper semantic modeling and governance, text-to-SQL services can achieve nearly 90% accuracy [1].
Real-Time Analytics and Embedded Intelligence
Real-time analytics has transformed the way organizations handle data, moving away from static, delayed reports to insights delivered the moment data is generated. Whether it’s tracking a customer’s journey on an e-commerce site, identifying equipment issues through sensors, or monitoring a delivery driver’s completed routes, real-time analytics enables businesses to act immediately. Instead of reacting to problems after they occur, organizations can now anticipate and prevent issues, like spotting customer churn or detecting machine failures as they unfold [21]. This shift opens the door to embedding intelligence directly into everyday applications.
Real-Time Data Freshness
To achieve real-time insights, businesses need infrastructure capable of handling sub-second query speeds. Techniques like prefix caching, speculative decoding, and intermediate state reuse help reduce query latency to under 100 milliseconds, even during high-demand periods [22]. This allows thousands of users to access live data simultaneously without performance dips.
A great example of this in action comes from Swiggy, India’s top food delivery platform. In September 2025, Swiggy adopted real-time intelligence to process clickstream and operational data instantly. Madhusudan Rao, Swiggy's CTO, shared:
"Fabric's Real-Time Intelligence empowers us to analyze clickstream and operational data instantly, helping us detect anomalies in real time" [21].
With this capability, Swiggy could monitor millions of orders per hour, ensuring they met delivery speed commitments for their vast customer base.
Between 2024 and 2025, the demand for real-time intelligence skyrocketed, with workloads increasing sixfold [21]. This shift from batch processing - where insights could take days or even weeks - to live data analysis has enabled teams to act as events happen. These immediate insights are paving the way for analytics to be seamlessly integrated into operational systems.
Embedded Analytics Use Cases
Building on the foundation of real-time data, embedded analytics places insights directly within the tools and workflows users rely on every day. Instead of requiring users to switch between operational tools and separate business intelligence (BI) platforms, embedded analytics tools deliver actionable data right where it’s needed.
In June 2025, Siemens Energy introduced an AI-powered chatbot that provided 25 R&D engineers with near-instant access to previously hard-to-find data. Tim Kessler, Head of Data, Models & Analytics at Siemens Energy, explained:
"The ability to unlock and democratize the data hidden in our data treasure trove has given us a distinct competitive edge" [9].
This tool significantly sped up research timelines by making critical data easily accessible.
Sonepar, a global distributor operating in 40 countries, also embraced this approach. In September 2025, the company integrated real-time intelligence into its e-commerce platform. Yann Shah, VP of Data, Analytics & AI at Sonepar, commented:
"At Sonepar, real-time capabilities are essential... With Microsoft Fabric and Real-Time Intelligence, we convert live data into swift actions" [21].
By embedding analytics within its customer-facing systems, Sonepar could transform live logistics data into immediate, actionable insights.
This move toward embedded analytics isn’t just about convenience - it’s a game-changer for how businesses operate. When analytics are built into the tools people already use, decisions are made faster, insights remain tied to their context, and workflows are uninterrupted. This integration fundamentally enhances how organizations compete in their respective markets.
Lean AI Strategy for Cost-Effective Analytics
Many organizations waste time and money chasing flashy but ineffective AI pilots. A Lean AI strategy shifts the focus to measurable results, like cutting costs, improving speed, or boosting quality [24][26].
Here’s a sobering statistic: 95% of AI initiatives fail to advance beyond the pilot stage. Why? Poor data quality and unclear ownership are the usual culprits [25]. As Bain & Company aptly explains:
"The basic rule of 'garbage in, garbage out' remains a feature of AI as much as any other digital solution" [25].
On top of data quality issues, fragmented ownership often derails these projects. This highlights the importance of building reusable, production-ready foundations instead of relying on isolated experiments.
A North American utility company offers a great example. Plagued by inconsistent data quality and unclear ownership, they mapped out their data maturity and launched specific pilots to trace data lineage. This disciplined approach paid off. They improved forecasting accuracy for customer load, gained 20% to 25% efficiency, and recovered nearly $10 million from billing discrepancies in just one year [25].
Another cost-saving measure is consumption-based pricing, which ties expenses to actual usage. This approach minimizes upfront costs and reduces operational overhead [12][6][24]. But to truly cut costs, organizations must treat data as modular assets instead of sprawling, unmanageable lakes.
Making Data Contextual and Reusable
Cost-effective AI analytics starts with treating data as modular assets. Tools like dbt allow teams to create reusable SQL models, cutting down on redundant work across AI initiatives [23][25]. For example, defining terms like "revenue" or "churn" once in a unified semantic layer ensures consistency across all AI systems, eliminating the need to rebuild logic for every new use case [23][12].
Another smart move? Incremental processing. Instead of reprocessing all data, only new data is handled, reducing both warehouse load and runtime costs [23]. Automating data quality monitoring within pipelines is also key. Catching issues early prevents costly fixes later on, whether in AI models or dashboards [23].
To avoid the pitfalls of fragmented data, assign clear domain ownership. Organizing data into business-aligned domains ensures specific teams are responsible for its quality and accessibility [25]. This approach keeps data production-ready and trustworthy, setting AI projects up for success.
Scaling Analytics Efficiently
Once you’ve built high-quality, reusable data assets, the next step is scaling - but it’s important to start small. Focus on high-impact pilots like sales pipeline analysis or supply chain monitoring. These targeted projects allow teams to prove value quickly and learn what works before rolling out more broadly [12].
Today, over 54% of operational leaders use AI in their infrastructure to automate processes and reduce costs [23]. AI is also transforming data preparation, traditionally the most time-consuming task for analysts. By automating data cleaning, schema mapping, and quality checks, organizations can shift analysts’ attention to uncovering insights rather than wrestling with raw data [27].
Looking ahead, the use of synthetic data and transfer learning could reduce the need for real data in AI projects by over 50% by 2025 [26]. Pair this with managed AI services (SaaS/PaaS), which eliminate the burden of infrastructure management, and you’ve got a recipe for rapid analytics scaling without ballooning costs [24].
AI-Native Platforms: The Future of Business Intelligence
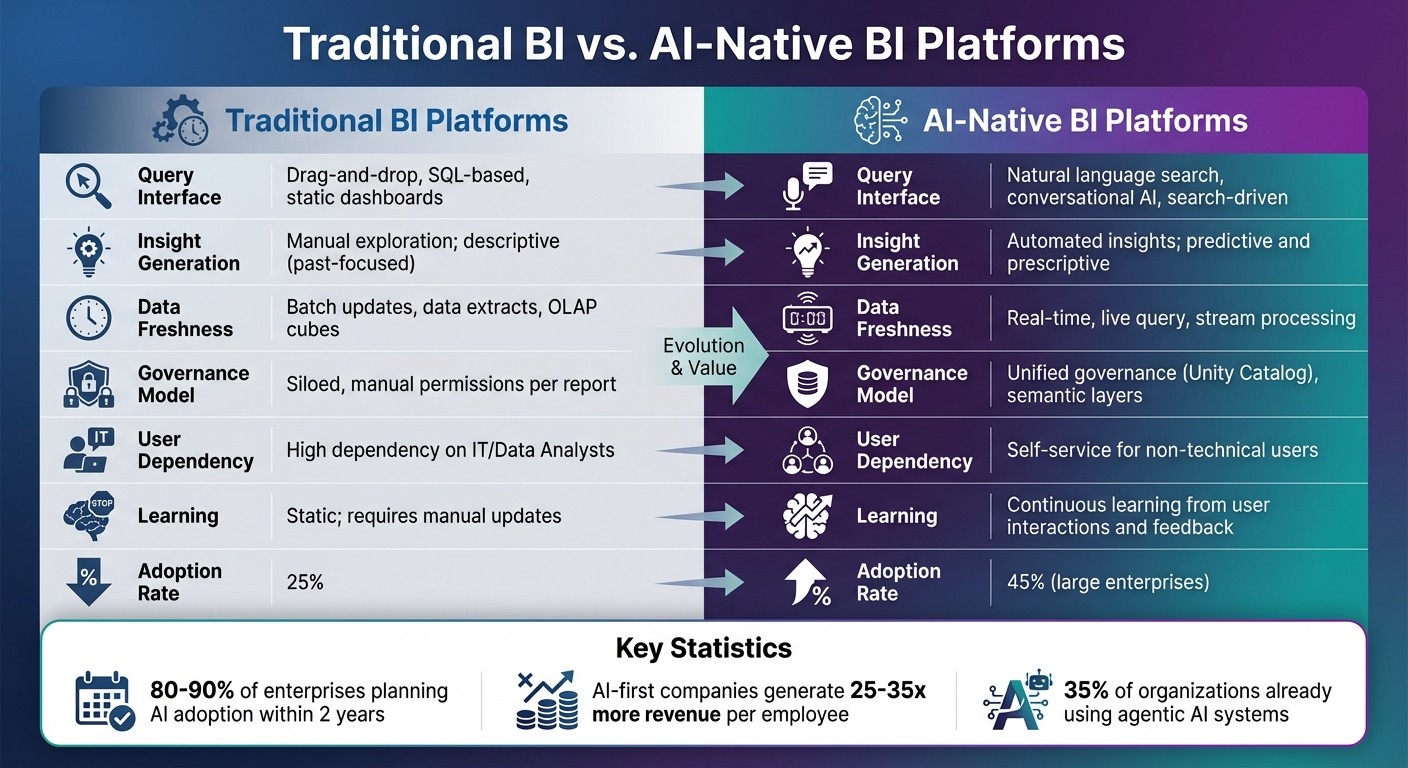
Traditional BI vs AI-Native BI Platforms Comparison
What Sets AI-Native Platforms Apart
AI-native platforms are reshaping how businesses interact with data. Unlike traditional BI tools that rely on static dashboards and drag-and-drop interfaces, these platforms offer search-driven interfaces and conversational analytics. They make data interaction feel as natural as chatting with a colleague, rather than navigating complex software [7][5]. This approach simplifies how users engage with data, thanks to intuitive, conversational interfaces.
Adoption rates tell the story. Traditional BI tools often struggle, with adoption rates dipping as low as 25% due to technical barriers [3]. AI-native platforms tackle this issue by allowing users to ask questions in plain English and receive immediate answers. These answers are powered by real SQL or Python code running against live data warehouses, eliminating the need for technical expertise.
Take Virgin Atlantic and SEGA Europe as examples. Virgin Atlantic reduced booking analysis times from weeks to mere hours, while SEGA Europe achieved insights ten times faster [5].
Tim Kessler, Head of Data, Models & Analytics at Siemens Energy, highlighted the transformative impact:
"This chatbot... has been a game changer for Siemens Energy. The ability to unlock and democratize the data hidden in our data treasure trove has given us a distinct competitive edge." [9]
AI-native platforms also excel by running analytics directly on governed data. This ensures real-time freshness and eliminates the delays of batch updates or reliance on OLAP cubes [5][7].
Traditional BI vs. AI-Native Platforms
The differences between traditional BI platforms and AI-native platforms are striking. Here’s a quick comparison:
Dimension | Traditional BI Platforms | AI-Native BI Platforms |
|---|---|---|
Query Interface | Drag-and-drop, SQL-based, static dashboards | Natural language search, conversational AI, search-driven |
Insight Generation | Manual exploration; descriptive (past-focused) | Automated insights; predictive and prescriptive |
Data Freshness | Batch updates, data extracts, OLAP cubes | Real-time, live query, stream processing |
Governance Model | Siloed, manual permissions per report | Unified governance (e.g., Unity Catalog), semantic layers |
User Dependency | High dependency on IT/Data Analysts | Self-service for non-technical users |
Learning | Static; requires manual updates | Continuous learning from user interactions and feedback |
These platforms represent a shift from static, IT-dependent dashboards to dynamic, user-driven analytics. Traditional systems often require IT teams to step in for every new query, but AI-native platforms empower users by democratizing access to data [9][3].
Even pricing models are evolving. Some AI-native platforms have moved away from per-seat licensing, instead charging only for compute usage. This change allows businesses to extend analytics access to all employees without worrying about additional licensing costs [7][5]. For many organizations, this makes enterprise-wide data access both practical and affordable.
Conclusion
The move from older business intelligence (BI) methods to AI-powered analytics isn’t just about upgrading technology - it’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with data. AI has turned BI into a forward-looking, predictive tool that’s accessible to everyone, from finance teams to marketing professionals, enabling smarter, faster decisions [3][2].
The numbers back up this transformation. Traditional BI tools often see low engagement rates, with only about 25% of users adopting them due to their complexity [3]. In contrast, 45% of large enterprises already use AI, and 80–90% are planning to adopt it within the next two years [2]. Companies leveraging AI-first strategies report generating 25 to 35 times more revenue per employee compared to those sticking with traditional methods [18]. These statistics highlight how quickly AI-driven analytics is reshaping the business landscape.
The next step in this evolution is agentic AI, which takes BI beyond analysis and into automated execution. As Boston Consulting Group (BCG) explains:
"If predictive AI is the left brain for logic and optimization, and generative AI the right brain for creativity and synthesis, then agentic AI serves as the executive function that turns creative probability into business impact" [18].
Currently, 35% of organizations are already using agentic AI systems, enabling BI platforms to not only analyze data but also autonomously observe, plan, and execute workflows [18].
Querio stands out in this rapidly evolving space by combining advanced AI features like natural language querying tools, automated insights, and real-time analytics with the governance and transparency enterprises need. Its adoption rates and performance metrics make it clear: implementing AI-driven BI isn’t just beneficial - it’s critical for staying competitive.
But success with AI-driven analytics isn’t just about adopting new tools. It requires a balanced strategy. The 10/20/70 rule serves as a guide: dedicate 10% of your effort to algorithms, 20% to building the tech infrastructure, and 70% to rethinking business processes and training teams [18]. By following this framework, businesses can turn data analytics into a company-wide strength, unlocking the full potential of their data.
FAQs
How does AI make business intelligence easier for non-technical users?
AI is transforming how businesses approach intelligence by making self-service data analysis easier and more intuitive. With natural language interfaces, users no longer need to rely on technical skills like writing SQL queries or managing datasets manually. Instead, they can ask questions or request visualizations in everyday language. The AI then takes care of generating reports, dashboards, or insights, giving employees across various departments the ability to explore data independently and make quicker, informed decisions.
Generative AI and conversational tools take this a step further. They handle complex analytical tasks and turn unstructured requests into clear, actionable insights. This shift reduces the need for data specialists and encourages a data-focused mindset, enabling more team members to play an active role in decision-making. By streamlining operations and allowing businesses to adapt swiftly to changing demands, AI is making BI tools easier to use and accessible to everyone.
What are the key advantages of using AI-powered business intelligence tools over traditional systems?
AI-powered business intelligence (BI) tools offer a fresh approach that outshines traditional systems in several ways. They simplify access to data insights by using natural language processing (NLP) and user-friendly interfaces. This means teams can explore and understand data more quickly, even without advanced technical expertise. As a result, businesses can make decisions faster and rely less on specialized analysts, giving more people across the organization the ability to work with data.
These tools also save time by automating tasks like creating data visualizations, spotting patterns, and generating reports. On top of that, AI delivers predictive insights and supports real-time decision-making, enabling businesses to foresee trends, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities with improved precision. By transforming static reports into dynamic insights that can be acted upon, AI-driven BI tools encourage a more flexible and data-focused way of working.
What role do governed semantic layers play in ensuring accurate and compliant AI-driven business intelligence?
Governed semantic layers play a key role in keeping data consistent and meeting compliance standards in AI-powered business intelligence (BI). By unifying data definitions, metrics, and business rules across an organization, they eliminate inconsistencies and provide a shared foundation. This ensures everyone is working with the same set of accurate and dependable data, which is crucial for generating reliable AI insights and making sound decisions.
Beyond improving data accuracy, semantic layers also help enforce compliance. They control access to sensitive information, ensuring only authorized individuals can view or edit specific datasets. Additionally, they maintain audit trails, which are essential for meeting regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. With a robust semantic layer in place, businesses can confidently integrate AI into their BI processes, knowing their data is both trustworthy and secure.

