
Tableau Einstein Copilot natural language query 2025 2026
Business Intelligence
Feb 9, 2026
Natural-language AI that turns plain-English questions into secure, grounded visual analytics, streamlining analysis for all users.
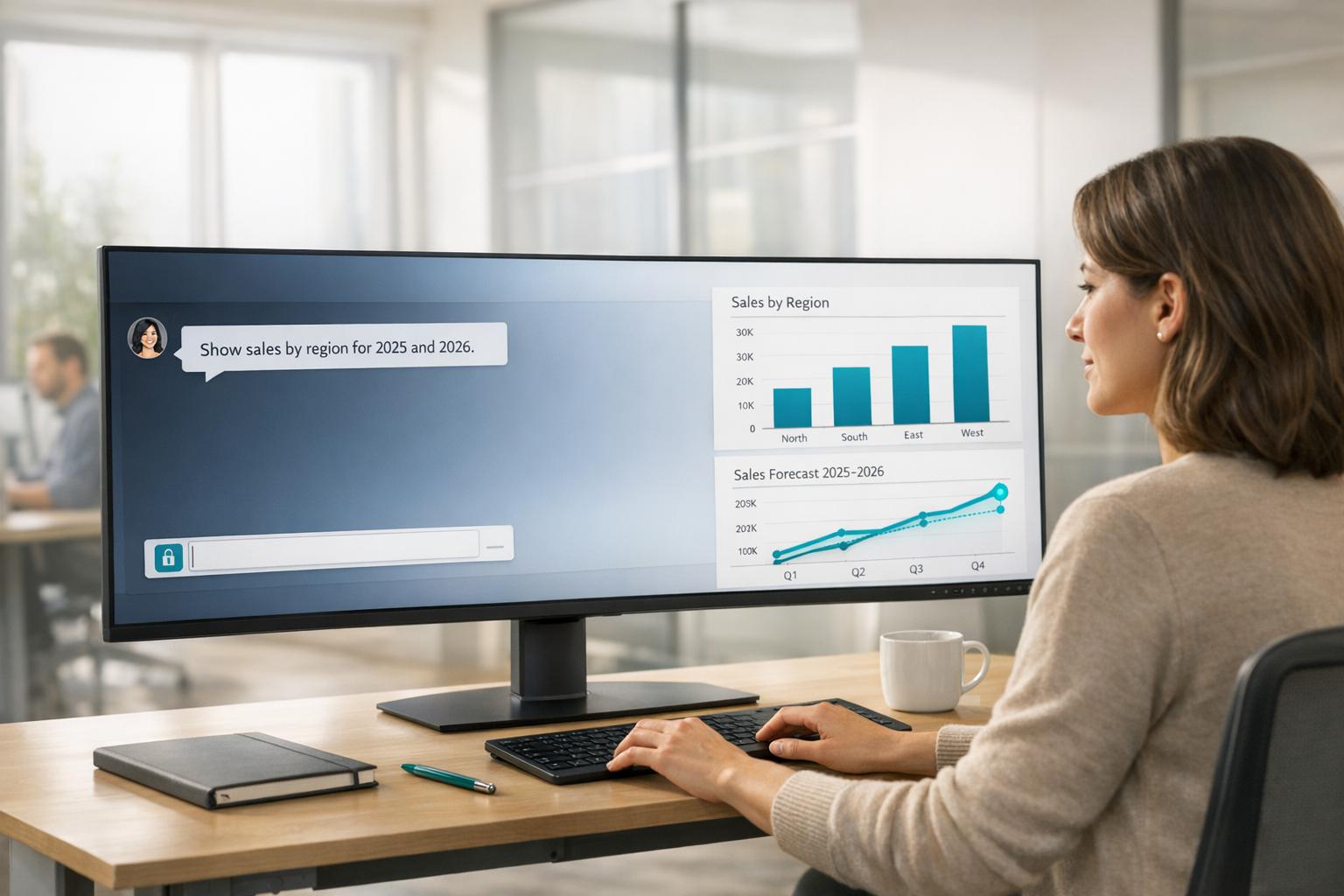

Tableau Agent (formerly Einstein Copilot) transforms data analysis by letting you ask questions in plain English, eliminating the need for manual visualization creation. Rebranded in October 2025, it simplifies analytics for both technical and non-technical users. Here’s what you need to know:
How It Works: Users type queries like, “Show me sales trends by region,” and Tableau translates them into visualizations using its proprietary languages, VizQL and Notional Spec.
AI Capabilities: Handles tasks like calculations, chart selection, and essential BI features like formula clarification with improved accuracy. It supports follow-up queries within a session, making analysis seamless.
Security Features: The Einstein Trust Layer ensures data privacy with features like PII masking and zero-data retention policies.
Core Technologies: Combines OpenAI models with Tableau’s visualization engine, using metadata grounding to deliver reliable insights.
Real-World Use: Non-technical users can explore data effortlessly, while analysts save time on repetitive tasks. Features like “Draft for Me” generate metadata descriptions, boosting productivity.
What is Einstein Copilot for Tableau?
How Natural Language Query Works in Tableau Einstein Copilot
How Tableau Agent Processes Natural Language Queries: A Step-by-Step Workflow
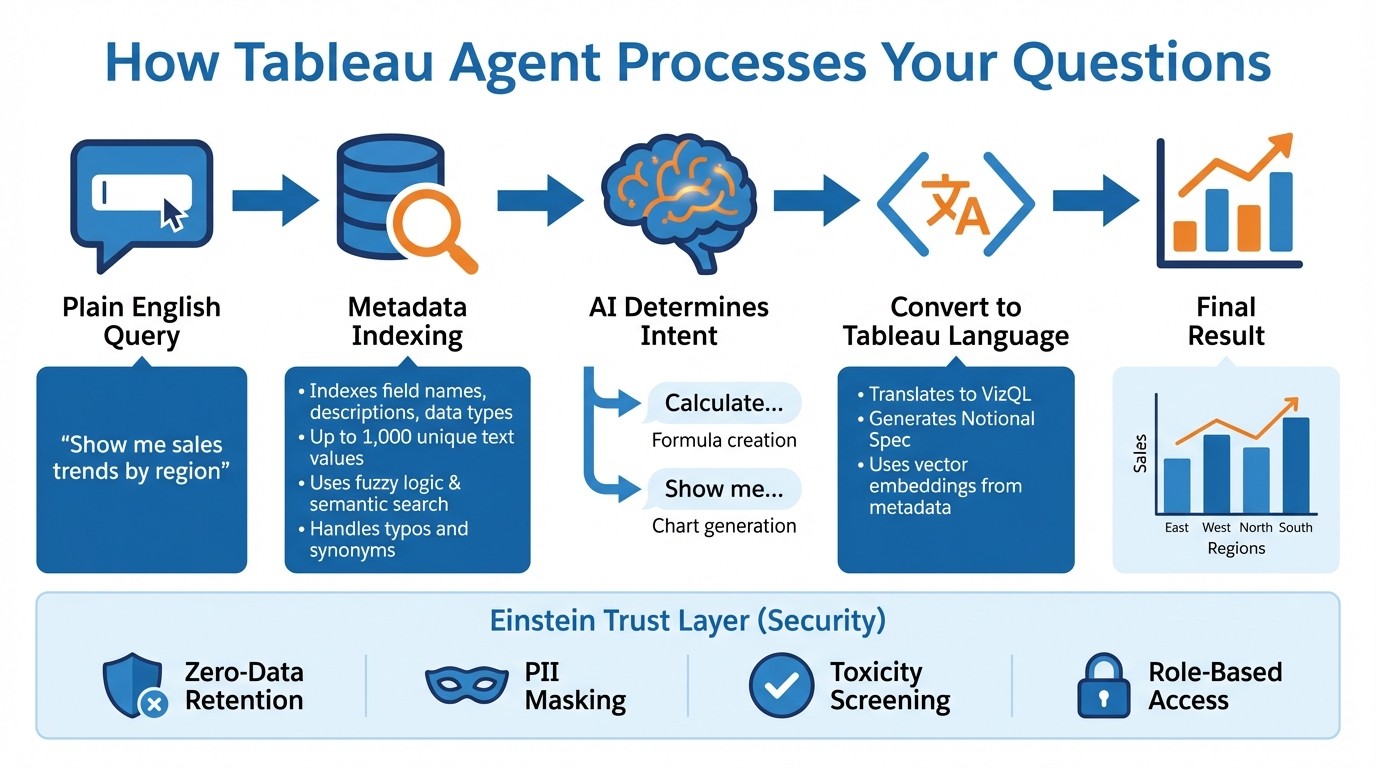
When you type a question into Tableau Agent, you're not directly querying the database. Instead, the system translates your plain language into VizQL and Notional Spec - Tableau's proprietary coding languages designed to create visualizations. Essentially, the AI generates Tableau-specific instructions based on your input [9].
The process begins with Dynamic Grounding, which indexes metadata like field names, descriptions, data types, and up to 1,000 unique text values. It uses fuzzy logic and semantic search to handle typos and recognize synonyms [1][2]. This allows the model to understand your query without needing access to the full dataset [1].
Next, intent classification determines whether you're asking to create a visualization or perform a calculation. Thanks to fine-tuned models, classification errors have been significantly reduced [3]. For better results, it's helpful to start prompts with action verbs. For example, use "Calculate..." for formulas or "Show me..." for charts [1].
The system also keeps a conversation history within the same worksheet, letting you build on previous queries. For instance, you could ask, "Show me sales trends by region", and then refine it with, "Now filter for technology products" [2]. However, this memory resets when you switch sheets or close the workbook [6]. This session memory enhances the user experience and demonstrates the advanced technologies behind Tableau Agent's natural language capabilities.
As John He, Vice President of Software Engineering at Tableau, explains: "Keeping the temperature lower reduces the risk of hallucination and provides users with reliable and accurate insights" [3].
Core Technologies Behind Tableau's Natural Language Features
Tableau Agent blends Large Language Models from OpenAI and Azure OpenAI with Tableau's visualization engine. By using vector embeddings derived from your data's metadata, the AI ensures its responses are based on real information instead of guesses [10].
The AI translates your queries into VizQL or Notional Spec instructions, which Tableau's visualization platform then converts into charts, tables, or calculations [9].
Tableau also employs an experimental platform called Zeus for ongoing improvement. Zeus includes a benchmarking system where one AI model evaluates another's output [3]. Additionally, lower temperature settings are used to limit creativity, reducing the chances of hallucinated or inaccurate responses [3].
These methods are further enhanced by the Einstein Trust Layer, which adds an extra layer of security and refinement to the query process.
The Einstein Trust Layer
The Einstein Trust Layer acts as a security filter between you and the language model, ensuring every query is processed securely. It enforces a zero-data retention policy, meaning that OpenAI and Azure OpenAI do not store your prompts or use them for training [9].
Before a query reaches the language model, pattern-based data masking automatically detects and replaces personally identifiable information (PII) - like names, email addresses, Social Security numbers, and IBAN codes - with generic placeholders [9]. Additionally, the system evaluates all inputs and outputs for toxicity, violence, and profanity to prevent harmful content [9].
Feature | Einstein Trust Layer Function |
|---|---|
Zero-Data Retention | Prevents LLM providers from storing or using customer data for training [9] |
Data Masking | Replaces PII with generic tokens before processing [9] |
Toxicity Scoring | Blocks harmful content and alerts users [9] |
Dynamic Grounding | Integrates relevant metadata to avoid hallucinations [9] |
The Trust Layer also works within Tableau's role-based controls and row-level security, ensuring AI-generated insights only use data you have permission to access [9]. For Tableau+ subscribers, an Audit Trail in Data 360 (formerly Data Cloud) logs every prompt and response for compliance and security reviews [9].
Honto Ming, Senior Product Manager at Tableau, highlights: "Trust does not only involve your data being secure. Trust also includes being confident that Tableau Agent will return accurate and safe results" [11].
It's worth noting that Tableau Server (version 2025.3+) operates differently. It connects directly to your own LLM provider and does not use the Einstein Trust Layer, leaving data protection and PII masking as your responsibility [6].
Using Natural Language Query in Tableau: Real Examples
Tableau Agent is changing how teams interact with data by allowing users to ask questions in plain English instead of manually creating visualizations. This approach has made analytics more accessible to a broader audience and sped up decision-making across various business functions.
With its advanced capabilities, Tableau Agent is delivering practical benefits in everyday analytics.
Data Exploration for Non-Technical Users
Non-technical users can explore data by simply typing questions into Tableau. For instance, a marketing manager might ask, "What month had the largest growth in number of donors?" and instantly see a time-series visualization - no formulas required [1][7]. Similarly, an operations analyst could type, "Calculate the business days between order and ship date," and Tableau Agent will generate the correct calculation syntax automatically [1].
The platform also suggests questions based on your data's metadata, making it easier to jump into analysis [1][7]. For example, when connected to a sales dataset, users might see prompts like "Show me the top 10 products based on profit" or "Compare sales to profit." They can click or modify these questions to start exploring right away [6][7].
Insights can be refined through follow-up questions. A user asking, "How many products sold per quarter?" might narrow the focus with "Show me electronics for Q4." This ability to build on earlier queries keeps the analysis flowing without having to start over.
These easy-to-use features enable faster, more informed decisions, as illustrated in the next example.
Better Decision-Making with AI-Generated Insights
Analytics teams leverage Tableau Agent to spot trends and streamline workflows more efficiently than traditional methods. The natural language interface simplifies complex tasks, such as calculating "the difference between case open and closed dates and rounding up to weeks" - tasks that used to require manual formula creation [1][7].
For data governance teams, the "Draft for Me" feature in Tableau Catalog is a game-changer. It generates descriptions for data sources, workbooks, and tables with a single click [4][5]. This enhances data discoverability within organizations and helps teams trust the datasets they use. As of October 2025, these AI-driven features no longer consume Einstein Request credits, making them more accessible to Tableau+ subscribers [1][7].
Additionally, the AI can explain existing calculations in plain language, helping users verify their accuracy and understand the logic behind even the most intricate formulas [1][4].
Adding Tableau's Natural Language Query to Your Workflows
Bringing Tableau Agent into your analytics workflows requires careful planning, especially when it comes to organizing and managing your data. Teams that set up clear data standards early on tend to see better AI accuracy and smoother adoption across their organizations.
The secret lies in creating workflows that align with AI needs, from data preparation to analysis. Tableau Agent integrates seamlessly at several points: Tableau Prep translates natural language into calculation syntax during data prep, Tableau Catalog produces metadata descriptions to enhance data discoverability, and Web Authoring supports conversational data exploration. When these elements are configured correctly, they work together to strengthen your overall analytics process.
A unified semantic and metrics foundation is essential for embedding AI-driven insights into your workflows effectively.
Using the Semantic Layer for Consistent Metrics
The Tableau Pulse Metrics Layer tackles a common problem in enterprise analytics: inconsistent metric definitions. When different teams calculate metrics like "revenue" or "active users" differently, it can undermine trust in the data. This centralized layer allows you to define each KPI once, ensuring that any updates automatically apply across all related metrics [12].
"The Tableau Pulse Metrics Layer is scalable - any changes that need to be made to the metric or KPI definition can be made once and will automatically apply to all Metrics related to that definition."
– Matthew Miller, Senior Director, Product Management, Tableau [12]
This setup eliminates the risk of conflicting data interpretations. Administrators maintain core semantic models, while analysts can tailor these models to specific needs, striking a balance between governance and flexibility [13].
How to Structure Data for Better AI Results
High-quality metadata is key to helping Tableau Agent understand your business context. Enhance metadata by adding clear field descriptions and comments in Tableau Desktop or Catalog. For instance, instead of a vague label like "rev_amt", use something more descriptive like "Monthly Revenue (USD)" and include details about how it's calculated.
Simplify your data sources by hiding irrelevant or duplicate fields (e.g., avoid both "customer_id" and "cust_id") and ensuring field names are unique and meaningful. Using data extracts (.hyper files) can also improve performance.
For more complex calculations, it's best to generate the calculation first and then request its visualization in a separate step. This structured method ensures that Tableau Agent delivers precise and dependable AI-driven insights.
Getting the Most from Tableau Einstein Copilot in 2025 and 2026
As Tableau Agent reshapes the way we approach analytics, knowing how to craft effective prompts and refine them is essential to draw meaningful insights from your data.
Creating well-thought-out prompts is the gateway to unlocking Tableau Agent's potential. The more precise your prompts, the more actionable the insights you'll receive. Harveen Kathuria, Senior Director of Product Management at Tableau, emphasizes this point:
"Tableau Agent is action-oriented and tries to determine user intent immediately, so try to be explicit about what you want it to do for you." [14]
The AI can remember up to 32,000 characters in a session, but starting a new worksheet resets the context, allowing for a fresh perspective. With Tableau Agent's dynamic querying capabilities, crafting clear and specific prompts becomes even more critical to fully utilize its features.
Writing Effective Natural Language Prompts
Specificity is key when writing natural language prompts. Vague questions like "show me the best products" can lead to unclear results. Instead, provide detailed instructions, such as "show me the top 10 products by profit." This approach ensures the AI understands exactly what you need. When working with calculations, break the process into steps. For example, first ask, "create a calculation called Profit Margin as (Profit/Sales)", and then follow up with, "show Profit Margin by Region as a bar chart."
Prompt Type | Less Effective | More Effective |
|---|---|---|
Ranking | "Show me the best products." | "Show me the top 10 products by Profit." |
Calculations | "What is the profit margin?" | "Create a calculation called Profit Margin as (Profit/Sales)." |
Time Series | "Show sales over time." | "Show monthly sales trends for the last 2 years as a line chart." |
Filtering | "Filter the data for tech." | "Filter the view to only show the 'Technology' category." |
Always specify the aggregation function you want - like SUM, AVERAGE, MEDIAN, or COUNT - rather than relying on the AI's default, which may not align with your business goals. Additionally, using the "Edit Synonyms" feature can simplify future queries by mapping common business terms (e.g., "car" or "vehicle") to technical field names.
Once you've set up clear prompts, refine them further to dig deeper into your data.
Refining Queries for Deeper Insights
Refining your queries is an iterative process that can uncover layers of insights. After generating an initial visualization, follow up with targeted refinements. For instance, you can ask the AI to "focus on the Technology category" or "show only Q4 2025 data" without needing to rephrase your entire query, as the AI retains context.
To explore your dataset's potential, use the AI-generated "Suggestions" feature on a blank worksheet. This can inspire questions your data might answer before you even start crafting prompts. If a calculation requires tweaking, you can open the Calculation Editor, describe the changes, and let the Agent update the syntax for you. This combination of natural language inputs and manual fine-tuning ensures both efficiency and accuracy.
"A key element of its functionality is the collaboration between advanced AI and human oversight... a human is always involved in the process, ensuring that all proposed responses are thoroughly checked before they are accepted."
– Harveen Kathuria, Senior Director, Product Management, Tableau [14]
As of October 2025, Tableau's AI features no longer consume Einstein Request credits, making experimentation more accessible [7]. This change allows teams to test different prompt styles without worrying about usage limits. By iterating on your prompts, you not only gain sharper insights but also enhance Tableau Agent's ability to simplify and streamline your analytics workflow.
Conclusion
Tableau Agent (formerly known as Einstein Copilot) has reshaped how organizations use AI in Tableau for analytics by making data exploration accessible to everyone - not just those with technical expertise. With its ability to interpret plain English queries and deliver accurate visualizations and calculations, this tool breaks down barriers to data analysis. It bridges the gap between raw data and actionable insights, all while maintaining strict security protocols.
The Einstein Trust Layer ensures that speed and accessibility don't compromise security. Features like PII masking and a zero-data-retention policy safeguard sensitive information, while grounding responses in actual dataset values ensures accuracy and reliability[6][7].
Looking ahead to 2025 and 2026, Tableau Agent offers benefits that go well beyond convenience. By automating repetitive tasks, it frees up analytics teams to focus on strategic insights. At the same time, business users gain the independence to explore data directly, without relying on IT or technical support. John He, Vice President of Software Engineering at Tableau, underscores this vision, emphasizing the goal of simplifying data analysis so that anyone can unlock its potential without extensive training or prior experience[8].
The transition from Einstein Request credits to Data 360 credits in October 2025 has further lowered the barriers to experimentation and exploration[7]. With this shift, continuous, conversational data exploration becomes a reality, allowing users to uncover deeper insights over time.
Whether you're crafting complex LOD calculations, generating metadata descriptions, or uncovering the questions your data can answer, Tableau Agent transforms analytics into a collaborative effort across an entire organization. This evolution is central to redefining business intelligence workflows for the years ahead. The key is leveraging AI outputs as a starting point, using structured prompts to guide the tool toward insights that truly matter to your business.
FAQs
How does Tableau Agent protect my data and ensure security?
Tableau Agent takes data privacy and security seriously, embedding these priorities into its design through the Einstein Trust Layer. This secure AI framework, part of the Salesforce platform, incorporates advanced security measures, strict data governance protocols, and agreements that protect sensitive information while enabling AI-driven functionalities.
When integrating with external Large Language Model (LLM) providers like OpenAI, Tableau ensures that security remains aligned with organizational policies. For Tableau Cloud users, agreements with providers such as Azure OpenAI guarantee that private data isn’t used to train external models. For those using Tableau Server, organizations can connect directly with their own API keys, retaining full control over both compliance and security.
By combining strong built-in safeguards with flexible integration options, Tableau Agent empowers organizations to manage their data securely while tapping into the potential of advanced AI tools.
What are the advantages of using natural language queries with Tableau's Einstein Copilot?
Tableau's Einstein Copilot makes interacting with data easier by allowing you to use natural language queries. Instead of relying on technical expertise, anyone on your team can ask questions or perform tasks using everyday language. This makes data analysis more approachable and accessible.
With simple commands, you can create visualizations, filter datasets, build calculations, or even identify trends - all without navigating complicated menus or writing a single line of code. This not only saves time but also streamlines workflows, helping your team focus on making smarter decisions faster.
Einstein Copilot also prioritizes security, ensuring your data stays private while delivering accurate and actionable insights. It's a user-friendly tool designed to improve efficiency and support better outcomes in your analytics processes.
How can non-technical users use Tableau Agent to analyze data?
Tableau Agent makes data analysis a breeze for non-technical users by letting them interact with it using plain, natural language commands. This AI-driven assistant takes on tasks like data cleaning, building visualizations, and uncovering insights, so you don’t need technical know-how to dive into advanced analytics.
For instance, you can ask Tableau Agent to craft a bar chart, spot trends, or break down a calculation. It handles the heavy lifting by translating your requests into actionable steps, such as creating calculated fields or running time series analyses. This not only simplifies data exploration but also empowers users to uncover insights faster and make smarter decisions with ease.

