The Best Tools for Natural Language to SQL
Business Intelligence
Dec 23, 2025
Compare top natural language-to-SQL tools—Querio, OpenAI Codex, Power BI Q&A, and BigQuery BI Engine—by compatibility, accuracy, visualization, and security.

Natural language to SQL tools let you query databases using plain English, making data accessible without needing to know SQL. These tools convert questions into SQL queries, helping teams save time and make decisions faster. They also provide transparency by showing the generated SQL, allowing users to verify and adjust queries as needed.
Here’s a quick look at four popular options:
Querio: Connects directly to Snowflake, BigQuery, and Postgres. It uses a context layer for accurate translations, offers built-in visualization, and prioritizes security with SOC 2 Type II compliance.
OpenAI Codex: Flexible for various databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL but requires custom setup. Accuracy depends on prompt quality and schema context.
Microsoft Power BI Q&A: Works with Power BI models and Azure SQL but will be retired in December 2026. It’s best for simple, ad-hoc queries.
Google BigQuery BI Engine: Optimized for BigQuery tables with schema-aware natural language processing and seamless integration with Google tools.
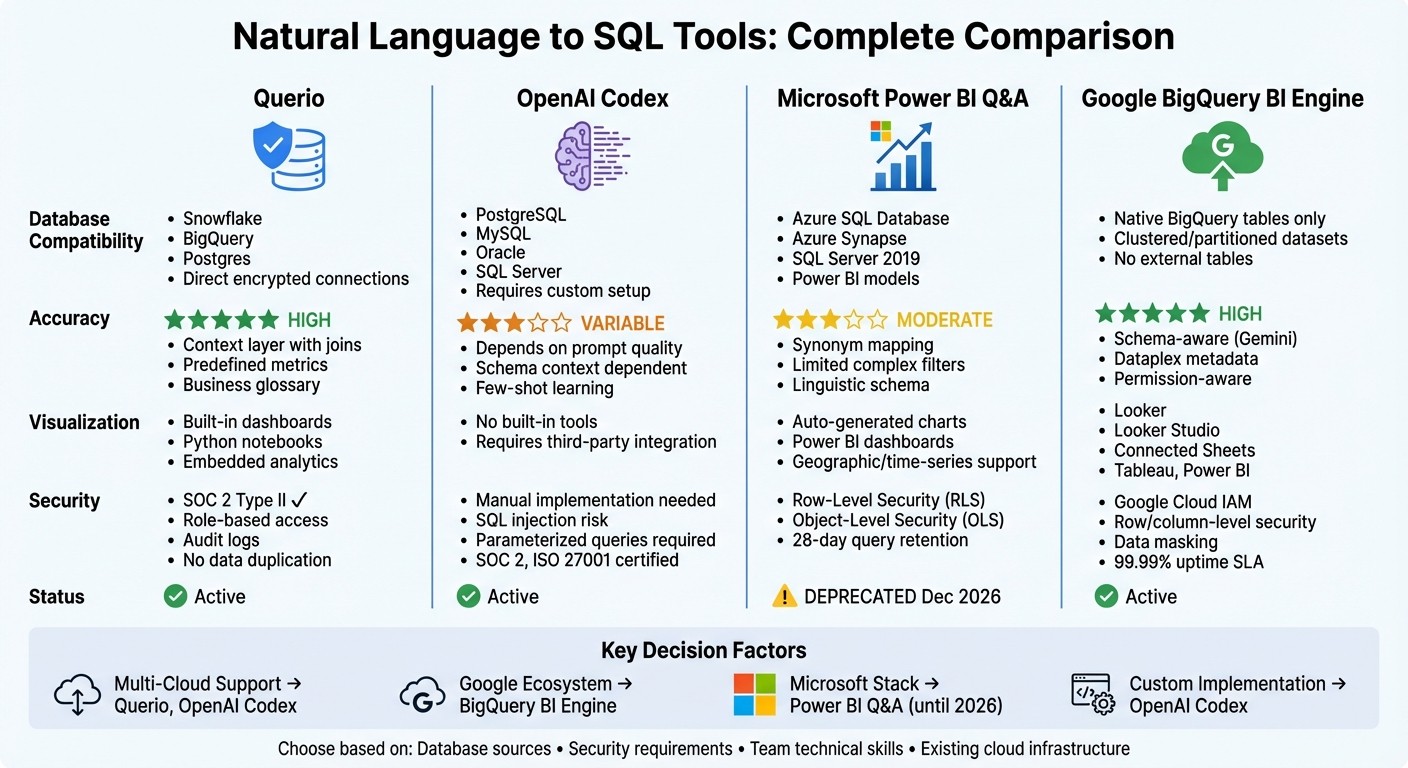
Quick Comparison:
Tool | Database Compatibility | Accuracy | Visualization & Integration | Security & Governance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Querio | Snowflake, BigQuery, Postgres | High (context layer) | Built-in dashboards, Python notebooks | SOC 2 Type II, encrypted connections |
OpenAI Codex | PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, etc. | Variable (prompt-based) | Requires third-party tools | Custom implementation required |
Power BI Q&A | Azure SQL, SQL Server | Moderate | Power BI dashboards | RLS, OLS, deprecated in 2026 |
BigQuery BI Engine | Native BigQuery tables | High (schema-aware) | Looker, Connected Sheets, Tableau | IAM roles, row/column-level security |
Each tool has strengths and trade-offs. Choose based on your data sources, security needs, and team’s technical skills.
Natural Language to SQL Tools Comparison: Features, Security, and Database Compatibility
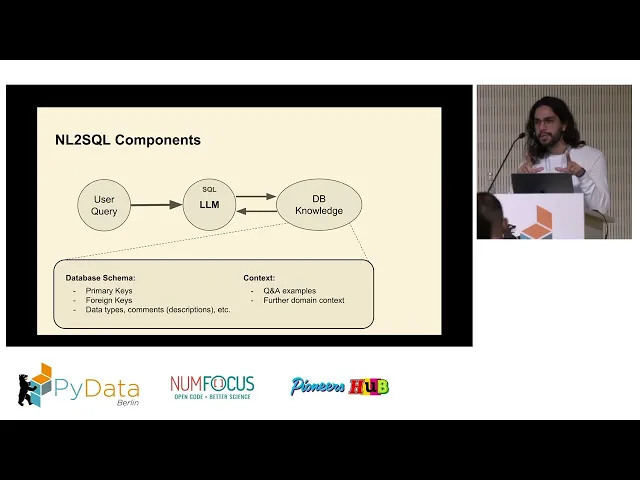
Building an AI Agent for Natural Language to SQL Query Execution on Live Databases
1. Querio
Querio is a cloud-based SaaS platform designed to help business users query databases without needing to write SQL. By connecting directly to your data warehouse using encrypted, read-only credentials, it eliminates the hassle of data duplication or complicated ETL pipelines. Plus, it ensures that all queries reflect the most up-to-date information.
Database Compatibility
Querio works seamlessly with Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Postgres, offering live connections to your databases. These live links ensure real-time data access and prevent synchronization headaches. For organizations with strict data residency rules, Querio also provides a self-hosted deployment option in addition to its cloud-based setup.
Natural Language Accuracy
One of Querio’s standout features is its context layer, where data teams can define table joins, business metrics, and terminology upfront. This ensures that natural language queries like “What were last quarter’s sales?” are accurately translated into SQL, producing consistent and error-free results. The platform’s AI engine takes plain English inputs and converts them into SQL while adhering to these predefined rules, keeping results uniform across the board.
Visualization and Integration
Querio makes data analysis more intuitive by instantly generating charts from natural language queries. For users needing advanced capabilities, it includes an integrated Python notebook for data science workflows. Additionally, its embedded analytics feature allows you to bring query functionality directly into your own SaaS products, enabling end users to analyze data without leaving your application. This combination caters to both non-technical users and those requiring deeper technical flexibility.
Governance and Security
With SOC 2 Type II compliance, Querio prioritizes security and governance. It enforces role-based access, encrypts data both in transit and at rest, and keeps a detailed log of every query. The context layer also ensures that business definitions and access rules are automatically applied, meeting even the strictest compliance standards. This solid security framework positions Querio as a strong contender among other leading data tools.
2. OpenAI Codex

OpenAI Codex is a generative AI model designed to convert natural language into SQL code. Essentially, it takes a system prompt - a summary of your database schema, including table names, columns, and relationships - and translates plain English queries into SQL statements. This ability makes Codex a powerful tool for navigating and querying various database systems.
Database Compatibility
Codex is built to work with a wide range of relational databases, including PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server (T-SQL), Oracle Database, and MySQL. It handles common database structures like tables, views, and foreign keys, as well as advanced features like Oracle Analytic Views. However, it's important to note that Codex only accesses schema metadata, not the actual data itself. This limitation can sometimes lead to inaccuracies when queries require understanding specific data values. As Microsoft's documentation highlights:
"Copilot might produce inaccurate results when the intent is to evaluate data. Copilot only has access to the database schema; none of the data is inside."
Natural Language Accuracy
The model's accuracy hinges on few-shot learning and schema linking. Including 3–5 example queries with their SQL translations in the prompt can greatly enhance its ability to interpret your database's specific dialect. For consistent results, set the model's temperature to 0; increasing the temperature can lead to syntax errors. Additionally, descriptive table and column names improve outcomes, as vague or cryptic naming conventions often confuse the model. Modern implementations also execute the generated SQL and refine it iteratively based on errors, improving reliability.
Governance and Security
OpenAI ensures robust security and compliance measures, including SOC 2 Type 2, ISO/IEC 27001, and CSA STAR Level 1 certifications. Data is encrypted using AES-256 at rest and TLS 1.2+ during transit. Importantly, API inputs and outputs are not used for model training. The platform complies with GDPR and CCPA, and for healthcare applications, Business Associate Agreements (BAA) are available to meet HIPAA requirements.
To minimize risks like SQL injection attacks, always use parameterized queries and apply post-processing filters to block destructive keywords such as 'DROP', 'DELETE', or 'TRUNCATE'. Leveraging read-only database views adds another layer of security, ensuring the AI can only access data without making any modifications.
3. Microsoft Power BI Q&A
Microsoft Power BI Q&A is one of several conversational analytics tools that transform plain English questions into SQL queries and visualizations. It works by creating an index of up to 1,000 model entities (like tables and fields) and as many as 5 million unique text values under 100 characters. This allows for real-time interpretation of user input.
Database Compatibility
Power BI Q&A supports three main data modes: Import mode, DirectQuery, and Live Connect. For DirectQuery, officially supported sources include Azure SQL Database, Azure Synapse Analytics, and SQL Server 2019. Live Connect is compatible with Azure Analysis Services and on-premises SQL Server Analysis Services. However, it does not work with DirectLake, Lakehouse Power BI datasets, or Power BI Report Server. For DirectQuery setups, the index refreshes automatically every day.
Natural Language Accuracy
The accuracy of Power BI Q&A depends on synonym mapping and language structures. It uses a built-in thesaurus to suggest synonyms, while administrators can customize synonyms for tables and columns using the "Teach Q&A" tool. Designers can also define phrasings in the linguistic schema to help the engine understand more complex relationships. For instance, they can specify what "popular" means in the context of "popular products." Assigning Data Categories - such as City, Country, or Date - helps the system interpret queries more effectively and select the right visualizations. Renaming tables and setting clear aggregation rules further enhance clarity.
Visualization and Integration
Power BI Q&A automatically generates visualizations based on the query results. For example, geographical data might result in a map, while time-series data could produce a line chart. Administrators can assign user-friendly labels to ensure charts are easy to understand. However, Microsoft has announced that Q&A features will be deprecated in December 2026. Users are encouraged to transition to Copilot for Power BI, which offers more advanced natural language processing capabilities.
Governance and Security
Power BI Q&A includes robust security measures such as Row-Level Security (RLS), ensuring users can only view data they are authorized to access. For models hosted in the Power BI service, Object-Level Security (OLS) is also supported. To guard against SQL injection attacks, the system uses parameterized queries and applies filters to block restricted keywords. User-submitted questions are stored for up to 28 days, as defined by tenant settings, allowing for review. Privacy levels - categorized as Private, Organizational, and Public - control how data is shared between sources. The "Private" level is specifically designed to protect sensitive information like PII or HR records.
4. Google BigQuery BI Engine
Google BigQuery BI Engine adds an in-memory runtime layer to BigQuery, enabling lightning-fast query responses for dashboards and business intelligence tasks. With Gemini in BigQuery, natural language capabilities are introduced, allowing users to generate SQL code automatically using prompts and metadata from the Dataplex Universal Catalog. Let’s take a closer look at how BI Engine works with different data setups and tools.
Database Compatibility
BI Engine is designed to work seamlessly with native BigQuery tables, including clustered and partitioned datasets. It integrates directly with the BigQuery API, so applications using standard REST, JDBC, or ODBC drivers can function without requiring code changes. However, it doesn’t support external tables in Cloud Storage, BigLake, or wildcard tables. The system ensures reliability with a 99.99% uptime SLA. For cost considerations, the free tier includes 10 GiB of storage and up to 1 TiB of query processing per month, while on-demand pricing begins at $6.25 per TiB scanned.
Natural Language Accuracy
With Gemini in BigQuery, plain English questions are converted into SQL by analyzing your data models and metadata. Providing schema descriptions enhances the system’s ability to understand the context of your tables and columns, improving accuracy. It also respects existing data permissions, ensuring users only access data they are authorized to view. For best results, use pre-joined or pre-aggregated data and mark frequently queried tables as "preferred" to prioritize them in the in-memory cache.
Visualization and Integration
BI Engine integrates effortlessly with Google tools like Looker, Looker Studio, and Connected Sheets, as well as third-party platforms like Tableau and Microsoft Power BI. To improve dashboard performance, partition tables by time so only relevant data is loaded into memory.
"BigQuery and Vertex AI have transformed our customer feedback process from a lengthy manual procedure to a near-instant natural language query, yielding insights in minutes."
Governance and Security
BI Engine takes advantage of BigQuery’s advanced security features, including row-level security, column-level security, and data masking. Access to Gemini’s features is managed through IAM roles, specifically the roles/cloudaicompanion.user role. Google ensures that customer prompts and SQL responses are not used to train its AI models without explicit permission. Additionally, all SQL generated through natural language queries is subject to the same audit logging and resource quotas as standard SQL queries. You can keep track of query patterns using BigQuery's INFORMATION_SCHEMA or Cloud Monitoring tools.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Each platform brings its own strengths and challenges, making it essential to evaluate how they align with your specific business needs. By understanding where these tools excel and where they might fall short, you can choose the one that best fits your workflow and priorities.
The table below provides a concise comparison of the key strengths and limitations of these tools across four important areas: database compatibility, natural language accuracy, visualization capabilities, and security features.
Tool | Database Compatibility | Natural Language Accuracy | Visualization & Integration | Security & Governance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Querio | Snowflake, BigQuery, Postgres (direct, encrypted, read-only connections) | High (context layer with joins, metrics, glossary) | Drag-and-drop dashboards; embedded analytics; AI Python notebooks | SOC 2 Type II; no data duplication; role-based access; audit logs |
OpenAI Codex | No native database connectivity (requires custom implementation) | Variable (depends on prompt quality and schema context) | No built-in visualization; requires third-party tools | Manual implementation; potential data use for training (plan dependent); SQL injection risk without parameterized queries |
Microsoft Power BI Q&A | Power BI Semantic Models; optimized for Azure and SQL Server | Moderate (limited support for multiple filter conditions) | High for visual outputs; integrates with Power BI dashboards | Row-Level Security (RLS) and Object-Level Security (OLS); 28-day question log retention; deprecated in December 2026 |
Google BigQuery BI Engine | Native BigQuery tables (clustered/partitioned); no external tables or BigLake | High with Gemini (schema-aware; uses Dataplex metadata) | Looker, Looker Studio, Connected Sheets, Tableau, Power BI | Google Cloud IAM; row/column-level security; data masking |
This breakdown highlights how each tool caters to different priorities, such as security, real-time accuracy, visualization features, and database integration.
For organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies, Power BI Q&A offers seamless integration but is being retired in December 2026 in favor of Copilot for Power BI. OpenAI Codex is highly adaptable but requires strong custom security measures, like parameterized queries, to mitigate risks such as SQL injection. Industry benchmarks, such as Spider 2.0, reveal that even advanced models solve only 21.3% of text-to-SQL tasks, underscoring the challenges of achieving consistent accuracy.
BigQuery BI Engine stands out for its schema awareness and integration within Google Cloud but is limited to BigQuery tables. Meanwhile, Querio provides direct, encrypted connections to multiple data warehouses without duplicating data, along with a governed context layer and a SOC 2 Type II compliance framework.
Conclusion
Our analysis highlights the distinct strengths of each natural language to SQL tool, helping you identify the best fit based on your team's needs, technical skills, and governance priorities.
Querio stands out for organizations requiring secure, encrypted connections to multiple data warehouses. Its governed context layer ensures consistent business definitions across teams, making it a great choice for companies prioritizing data accuracy and compliance.
OpenAI Codex offers unmatched flexibility for technical teams ready to handle custom implementations. However, it lacks built-in security features, so additional safeguards are necessary. This tool is well-suited for prototyping or teams with strong engineering resources.
Microsoft Power BI Q&A is an excellent option for organizations already using Microsoft technologies. It simplifies basic, ad-hoc queries for straightforward questions, though more complex analysis still requires manual dashboard creation in Power BI Desktop.
Lastly, Google BigQuery BI Engine excels with its schema awareness and seamless integration within Google Cloud. It's a natural fit for teams working with BigQuery tables and standardized on Google’s ecosystem.
Each tool brings unique strengths and trade-offs to the table. Consider what matters most to your organization - whether it’s multi-cloud support, licensing flexibility, or strict audit requirements - and choose the solution that aligns with your goals.
FAQs
How do tools that convert natural language to SQL ensure accurate queries?
Natural language-to-SQL (NL2SQL) tools work by aligning the generated SQL code with the specific structure of the database. They examine the database schema - tables, columns, and their relationships - to ensure the queries they produce fit the database's framework. This approach reduces the chance of errors and avoids issues with generic or incompatible syntax.
To improve accuracy even further, many of these tools validate the generated queries. They perform syntax checks and run test queries on sample data to catch potential problems. If something doesn't align, the system can either refine the query automatically or ask the user for clarification, creating a feedback loop that helps fine-tune the results. For additional assurance, users are often encouraged to review the query themselves and use features like explain-SQL views, which break down how the natural language input was converted into SQL commands.
How do natural language-to-SQL tools ensure data security?
Natural language-to-SQL tools prioritize keeping your data safe with a range of advanced security measures. These include encryption to secure data during transfer and storage, role-based access controls to limit who can access your database, and audit logs that record every query and user action, providing a clear trail of activity.
Platforms like Querio go a step further by being SOC 2 Type II certified, which means their security protocols have been independently assessed to meet rigorous standards for data privacy and confidentiality. On top of this, they implement responsible-use policies to reduce data exposure, such as restricting access to sensitive information. These combined efforts let you query databases intuitively and efficiently without compromising on security.
What is the best tool for working with Google Cloud services?
If you're seeking an easy way to work with Google Cloud services, Google BigQuery AI (powered by Gemini) might be exactly what you need. Built to function directly within BigQuery, it works effortlessly with other Google Cloud tools like Vertex AI and Looker Studio.
This platform takes the hassle out of data analysis, offering AI-powered query generation and quick insights while giving you direct access to your datasets stored in the Google Cloud environment. Since it eliminates the need for external connectors, it’s a streamlined and efficient option for those already using Google Cloud products.

